|
|
| (252 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | ==Abiotic Reduction of Munitions Constituents== | + | ==PFAS Treatment by Anion Exchange== |
| − | Munition compounds (MCs) often contain one or more nitro (-NO<sub>2</sub>) functional groups which makes them susceptible to abiotic reduction, i.e., transformation by accepting electrons from a chemical electron donor. In soil and groundwater, the most prevalent electron donors are natural organic carbon and iron minerals. Understanding the kinetics and mechanisms of abiotic reduction of MCs by carbon and iron constituents in soil is not only essential for evaluating the environmental fate of MCs but also key to developing cost-efficient remediation strategies. This article summarizes the recent advances in our understanding of MC reduction by carbon and iron based reductants.
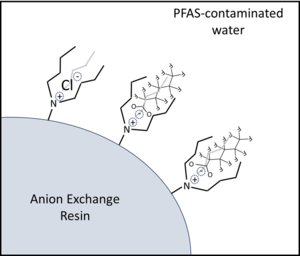
| + | [[Wikipedia: Ion exchange | Anion exchange]] has emerged as one of the most effective and economical technologies for treatment of water contaminated by [[Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) | per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)]]. Anion exchange resins (AERs) are polymer beads (0.5–1 mm diameter) incorporating cationic adsorption sites that attract anionic PFAS by a combination of electrostatic and hydrophobic mechanisms. Both regenerable and single-use resin treatment systems are being investigated, and results from pilot-scale studies show that AERs can treat much greater volumes of PFAS-contaminated water than comparable amounts of [[Wikipedia: Activated carbon | granular activated carbon (GAC)]] adsorbent media. Life cycle treatment costs and environmental impacts of anion exchange and other adsorbent technologies are highly dependent upon the treatment criteria selected by site managers to determine when media is exhausted and requires replacement or regeneration. |
| | <div style="float:right;margin:0 0 2em 2em;">__TOC__</div> | | <div style="float:right;margin:0 0 2em 2em;">__TOC__</div> |
| | | | |
| | '''Related Article(s):''' | | '''Related Article(s):''' |
| − | *[[Munitions Constituents]] | + | *[[Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS)]] |
| − | *[[Munitions Constituents - Alkaline Degradation]] | + | *[[PFAS Sources]] |
| | + | *[[PFAS Transport and Fate]] |
| | + | *[[PFAS Ex Situ Water Treatment]] |
| | + | *[[Supercritical Water Oxidation (SCWO)]] |
| | + | *[[PFAS Treatment by Electrical Discharge Plasma]] |
| | | | |
| | '''Contributor(s):''' | | '''Contributor(s):''' |
| − | *Dr. Jimmy Murillo-Gelvez | + | *Dr. Timothy J. Strathmann |
| − | *Paula Andrea Cárdenas-Hernández | + | *Dr. Anderson Ellis |
| − | *Dr. Pei Chiu | + | *Dr. Treavor H. Boyer |
| | | | |
| | '''Key Resource(s):''' | | '''Key Resource(s):''' |
| − | * Schwarzenbach, Gschwend, and Imboden, 2016. Environmental Organic Chemistry, 3rd ed.<ref name="Schwarzenbach2016">Schwarzenbach, R.P., Gschwend, P.M., and Imboden, D.M., 2016. Environmental Organic Chemistry, 3rd Edition. John Wiley and Sons, Ltd, 1024 pages. ISBN: 978-1-118-76723-8</ref> | + | *Anion Exchange Resin Removal of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) from Impacted Water: A Critical Review<ref name="BoyerEtAl2021a">Boyer, T.H., Fang, Y., Ellis, A., Dietz, R., Choi, Y.J., Schaefer, C.E., Higgins, C.P., Strathmann, T.J., 2021. Anion Exchange Resin Removal of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) from Impacted Water: A Critical Review. Water Research, 200, Article 117244. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.117244 doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117244] [[Media: BoyerEtAl2021a.pdf | Open Access Manuscript.pdf]]</ref> |
| | + | |
| | + | *Regenerable Resin Sorbent Technologies with Regenerant Solution Recycling for Sustainable Treatment of PFAS; SERDP Project ER18-1063 Final Report<ref>Strathmann, T.J., Higgins, C.P., Boyer, T., Schaefer, C., Ellis, A., Fang, Y., del Moral, L., Dietz, R., Kassar, C., Graham, C, 2023. Regenerable Resin Sorbent Technologies with Regenerant Solution Recycling for Sustainable Treatment of PFAS; SERDP Project ER18-1063 Final Report. 285 pages. [https://serdp-estcp.org/projects/details/d3ede38b-9f24-4b22-91c9-1ad634aa5384 Project Website] [[Media: ER18-1063.pdf | Report.pdf]]</ref> |
| | | | |
| | ==Introduction== | | ==Introduction== |
| − | [[File:AbioMCredFig1.PNG | thumb |left|300px|Figure 1. Common munitions compounds. TNT and RDX are legacy explosives. DNAN, NTO, and NQ are insensitive MCs (IMCs) widely used as replacement for legacy explosives.]] | + | [[File:StrathmannFig1.png | thumb |300px|Figure 1. Illustration of PFAS adsorption by anion exchange resins (AERs). Incorporation of longer alkyl group side chains on the cationic quaternary amine functional groups leads to PFAS-resin hydrophobic interactions that increase resin selectivity for PFAS over inorganic anions like Cl<sup>-</sup>.]] |
| − | Legacy and insensitive MCs (Figure 1.) are susceptible to reductive transformation in soil and groundwater. Many redox-active constituents in the subsurface, especially those containing organic carbon, Fe(II), and sulfur can mediate MC reduction. Specific examples include Fe(II)-organic complexes<ref name="Naka2006">Naka, D., Kim, D., and Strathmann, T.J., 2006. Abiotic Reduction of Nitroaromatic Compounds by Aqueous Iron(II)−Catechol Complexes. Environmental Science and Technology 40(9), pp. 3006–3012. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es060044t DOI: 10.1021/es060044t]</ref><ref name="Naka2008">Naka, D., Kim, D., Carbonaro, R.F., and Strathmann, T.J., 2008. Abiotic reduction of nitroaromatic contaminants by iron(II) complexes with organothiol ligands. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 27(6), pp. 1257–1266. [https://doi.org/10.1897/07-505.1 DOI: 10.1897/07-505.1]</ref><ref name="Hartenbach2008">Hartenbach, A.E., Hofstetter, T.B., Aeschbacher, M., Sander, M., Kim, D., Strathmann, T.J., Arnold, W.A., Cramer, C.J., and Schwarzenbach, R.P., 2008. Variability of Nitrogen Isotope Fractionation during the Reduction of Nitroaromatic Compounds with Dissolved Reductants. Environmental Science and Technology 42(22), pp. 8352–8359. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es801063u DOI: 10.1021/es801063u]</ref><ref name="Kim2009">Kim, D., Duckworth, O.W., and Strathmann, T.J., 2009. Hydroxamate siderophore-promoted reactions between iron(II) and nitroaromatic groundwater contaminants. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 73(5), pp. 1297–1311. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2008.11.039 DOI: 10.1016/j.gca.2008.11.039]</ref><ref name="Kim2007">Kim, D., and Strathmann, T.J., 2007. Role of Organically Complexed Iron(II) Species in the Reductive Transformation of RDX in Anoxic Environments. Environmental Science and Technology, 41(4), pp. 1257–1264. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es062365a DOI: 10.1021/es062365a]</ref>, iron oxides in the presence of aqueous Fe(II)<ref name="Colón2006">Colón, D., Weber, E.J., and Anderson, J.L., 2006. QSAR Study of the Reduction of Nitroaromatics by Fe(II) Species. Environmental Science and Technology, 40(16), pp. 4976–4982. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es052425x DOI: 10.1021/es052425x]</ref><ref name="Luan2013">Luan, F., Xie, L., Li, J., and Zhou, Q., 2013. Abiotic reduction of nitroaromatic compounds by Fe(II) associated with iron oxides and humic acid. Chemosphere, 91(7), pp. 1035–1041. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.070 DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.070]</ref><ref name="Gorski2016">Gorski, C.A., Edwards, R., Sander, M., Hofstetter, T.B., and Stewart, S.M., 2016. Thermodynamic Characterization of Iron Oxide–Aqueous Fe<sup>2+</sup> Redox Couples. Environmental Science and Technology, 50(16), pp. 8538–8547. [https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b02661 DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.6b02661]</ref><ref name="Fan2016">Fan, D., Bradley, M.J., Hinkle, A.W., Johnson, R.L., and Tratnyek, P.G., 2016. Chemical Reactivity Probes for Assessing Abiotic Natural Attenuation by Reducing Iron Minerals. Environmental Science and Technology, 50(4), pp. 1868–1876. [https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b05800 DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.5b05800]</ref><ref name="Jones2016">Jones, A.M., Kinsela, A.S., Collins, R.N., and Waite, T.D., 2016. The reduction of 4-chloronitrobenzene by Fe(II)-Fe(III) oxide systems - correlations with reduction potential and inhibition by silicate. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 320, pp. 143–149. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.08.031 DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.08.031]</ref><ref name="Klausen1995">Klausen, J., Troeber, S.P., Haderlein, S.B., and Schwarzenbach, R.P., 1995. Reduction of Substituted Nitrobenzenes by Fe(II) in Aqueous Mineral Suspensions. Environmental Science and Technology, 29(9), pp. 2396–2404. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es00009a036 DOI: 10.1021/es00009a036]</ref><ref name="Strehlau2016">Strehlau, J.H., Stemig, M.S., Penn, R.L., and Arnold, W.A., 2016. Facet-Dependent Oxidative Goethite Growth As a Function of Aqueous Solution Conditions. Environmental Science and Technology, 50(19), pp. 10406–10412. [https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b02436 DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.6b02436]</ref><ref name="Elsner2004">Elsner, M., Schwarzenbach, R.P., and Haderlein, S.B., 2004. Reactivity of Fe(II)-Bearing Minerals toward Reductive Transformation of Organic Contaminants. Environmental Science and Technology, 38(3), pp. 799–807. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es0345569 DOI: 10.1021/es0345569]</ref><ref name="Colón2008">Colón, D., Weber, E.J., and Anderson, J.L., 2008. Effect of Natural Organic Matter on the Reduction of Nitroaromatics by Fe(II) Species. Environmental Science and Technology, 42(17), pp. 6538–6543. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es8004249 DOI: 10.1021/es8004249]</ref><ref name="Stewart2018">Stewart, S.M., Hofstetter, T.B., Joshi, P. and Gorski, C.A., 2018. Linking Thermodynamics to Pollutant Reduction Kinetics by Fe<sup>2+</sup> Bound to Iron Oxides. Environmental Science and Technology, 52(10), pp. 5600–5609. [https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b00481 DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.8b00481] [https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/acs.est.8b00481 Open access article.]</ref><ref name="Klupinski2004">Klupinski, T.P., Chin, Y.P., and Traina, S.J., 2004. Abiotic Degradation of Pentachloronitrobenzene by Fe(II): Reactions on Goethite and Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Environmental Science and Technology, 38(16), pp. 4353–4360. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es035434j DOI: 10.1021/es035434j]</ref>, magnetite<ref name="Klausen1995"/><ref name="Elsner2004"/><ref name="Heijman1993">Heijman, C.G., Holliger, C., Glaus, M.A., Schwarzenbach, R.P., and Zeyer, J., 1993. Abiotic Reduction of 4-Chloronitrobenzene to 4-Chloroaniline in a Dissimilatory Iron-Reducing Enrichment Culture. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 59(12), pp. 4350–4353. [https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.59.12.4350-4353.1993 DOI: 10.1128/aem.59.12.4350-4353.1993] [https://journals.asm.org/doi/reader/10.1128/aem.59.12.4350-4353.1993 Open access article.]</ref><ref name="Gorski2009">Gorski, C.A., and Scherer, M.M., 2009. Influence of Magnetite Stoichiometry on Fe<sup>II</sup> Uptake and Nitrobenzene Reduction. Environmental Science and Technology, 43(10), pp. 3675–3680. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es803613a DOI: 10.1021/es803613a]</ref><ref name="Gorski2010">Gorski, C.A., Nurmi, J.T., Tratnyek, P.G., Hofstetter, T.B. and Scherer, M.M., 2010. Redox Behavior of Magnetite: Implications for Contaminant Reduction. Environmental Science and Technology, 44(1), pp. 55–60. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es9016848 DOI: 10.1021/es9016848]</ref>, Fe(II)-bearing clays<ref name="Hofstetter2006">Hofstetter, T.B., Neumann, A., and Schwarzenbach, R.P., 2006. Reduction of Nitroaromatic Compounds by Fe(II) Species Associated with Iron-Rich Smectites. Environmental Science and Technology, 40(1), pp. 235–242. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es0515147 DOI: 10.1021/es0515147]</ref><ref name="Schultz2000">Schultz, C. A., and Grundl, T.J., 2000. pH Dependence on Reduction Rate of 4-Cl-Nitrobenzene by Fe(II)/Montmorillonite Systems. Environmental Science and Technology 34(17), pp. 3641–3648. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es990931e DOI: 10.1021/es990931e]</ref><ref name="Luan2015a">Luan, F., Gorski, C.A., and Burgos, W.D., 2015. Linear Free Energy Relationships for the Biotic and Abiotic Reduction of Nitroaromatic Compounds. Environmental Science and Technology, 49(6), pp. 3557–3565. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es5060918 DOI: 10.1021/es5060918]</ref><ref name="Luan2015b">Luan, F., Liu, Y., Griffin, A.M., Gorski, C.A. and Burgos, W.D., 2015. Iron(III)-Bearing Clay Minerals Enhance Bioreduction of Nitrobenzene by ''Shewanella putrefaciens'' CN32. Environmental Science and Technology, 49(3), pp. 1418–1426. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es504149y DOI: 10.1021/es504149y]</ref><ref name="Hofstetter2003">Hofstetter, T.B., Schwarzenbach, R.P. and Haderlein, S.B., 2003. Reactivity of Fe(II) Species Associated with Clay Minerals. Environmental Science and Technology, 37(3), pp. 519–528. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es025955r DOI: 10.1021/es025955r]</ref><ref name="Neumann2008">Neumann, A., Hofstetter, T.B., Lüssi, M., Cirpka, O.A., Petit, S., and Schwarzenbach, R.P., 2008. Assessing the Redox Reactivity of Structural Iron in Smectites Using Nitroaromatic Compounds As Kinetic Probes. Environmental Science and Technology, 42(22), pp. 8381–8387. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es801840x DOI: 10.1021/es801840x]</ref><ref name="Hofstetter2008">Hofstetter, T.B., Neumann, A., Arnold, W.A., Hartenbach, A.E., Bolotin, J., Cramer, C.J., and Schwarzenbach, R.P., 2008. Substituent Effects on Nitrogen Isotope Fractionation During Abiotic Reduction of Nitroaromatic Compounds. Environmental Science and Technology, 42(6), pp. 1997–2003. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es702471k DOI: 10.1021/es702471k]</ref>, hydroquinones (as surrogates of natural organic matter)<ref name="Hartenbach2008"/><ref name="Schwarzenbach1990">Schwarzenbach, R.P., Stierli, R., Lanz, K., and Zeyer, J., 1990. Quinone and Iron Porphyrin Mediated Reduction of Nitroaromatic Compounds in Homogeneous Aqueous Solution. Environmental Science and Technology, 24(10), pp. 1566–1574. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es00080a017 DOI: 10.1021/es00080a017]</ref><ref name="Tratnyek1989">Tratnyek, P.G., and Macalady, D.L., 1989. Abiotic Reduction of Nitro Aromatic Pesticides in Anaerobic Laboratory Systems. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 37(1), pp. 248–254. [https://doi.org/10.1021/jf00085a058 DOI: 10.1021/jf00085a058]</ref><ref name="Hofstetter1999">Hofstetter, T.B., Heijman, C.G., Haderlein, S.B., Holliger, C. and Schwarzenbach, R.P., 1999. Complete Reduction of TNT and Other (Poly)nitroaromatic Compounds under Iron-Reducing Subsurface Conditions. Environmental Science and Technology, 33(9), pp. 1479–1487. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es9809760 DOI: 10.1021/es9809760]</ref><ref name="Murillo-Gelvez2019">Murillo-Gelvez, J., Hickey, K.P., Di Toro, D.M., Allen, H.E., Carbonaro, R.F., and Chiu, P.C., 2019. Experimental Validation of Hydrogen Atom Transfer Gibbs Free Energy as a Predictor of Nitroaromatic Reduction Rate Constants. Environmental Science and Technology, 53(10), pp. 5816–5827. [https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b00910 DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.9b00910]</ref><ref name="Niedźwiecka2017">Niedźwiecka, J.B., Drew, S.R., Schlautman, M.A., Millerick, K.A., Grubbs, E., Tharayil, N. and Finneran, K.T., 2017. Iron and Electron Shuttle Mediated (Bio)degradation of 2,4-Dinitroanisole (DNAN). Environmental Science and Technology, 51(18), pp. 10729–10735. [https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b02433 DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.7b02433]</ref><ref name="Kwon2006">Kwon, M.J., and Finneran, K.T., 2006. Microbially Mediated Biodegradation of Hexahydro-1,3,5-Trinitro-1,3,5- Triazine by Extracellular Electron Shuttling Compounds. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72(9), pp. 5933–5941. [https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00660-06 DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00660-06] [https://journals.asm.org/doi/reader/10.1128/AEM.00660-06 Open access article.]</ref>, dissolved organic matter<ref name="Dunnivant1992">Dunnivant, F.M., Schwarzenbach, R.P., and Macalady, D.L., 1992. Reduction of Substituted Nitrobenzenes in Aqueous Solutions Containing Natural Organic Matter. Environmental Science and Technology, 26(11), pp. 2133–2141. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es00035a010 DOI: 10.1021/es00035a010]</ref><ref name="Luan2010">Luan, F., Burgos, W.D., Xie, L., and Zhou, Q., 2010. Bioreduction of Nitrobenzene, Natural Organic Matter, and Hematite by Shewanella putrefaciens CN32. Environmental Science and Technology, 44(1), pp. 184–190. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es901585z DOI: 10.1021/es901585z]</ref><ref name="Murillo-Gelvez2021">Murillo-Gelvez, J., di Toro, D.M., Allen, H.E., Carbonaro, R.F., and Chiu, P.C., 2021. Reductive Transformation of 3-Nitro-1,2,4-triazol-5-one (NTO) by Leonardite Humic Acid and Anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate (AQDS). Environmental Science and Technology, 55(19), pp. 12973–12983. [https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c03333 DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.1c03333]</ref>, black carbon<ref name="Oh2013">Oh, S.-Y., Son, J.G., and Chiu, P.C., 2013. Biochar-Mediated Reductive Transformation of Nitro Herbicides and Explosives. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 32(3), pp. 501–508. [https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2087 DOI: 10.1002/etc.2087] [https://setac.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/etc.2087 Open access article.]</ref><ref name="Oh2009">Oh, S.-Y., and Chiu, P.C., 2009. Graphite- and Soot-Mediated Reduction of 2,4-Dinitrotoluene and Hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine. Environmental Science & Technology, 43(18), pp. 6983–6988. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es901433m DOI: 10.1021/es901433m]</ref><ref name="Xu2015">Xu, W., Pignatello, J.J., and Mitch, W.A., 2015. Reduction of Nitroaromatics Sorbed to Black Carbon by Direct Reaction with Sorbed Sulfides. Environmental Science and Technology, 49(6), pp. 3419–3426. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es5045198 DOI: 10.1021/es5045198]</ref><ref name="Oh2002">Oh, S.-Y., Cha, D.K., and Chiu, P.C., 2002. Graphite-Mediated Reduction of 2,4-Dinitrotoluene with Elemental Iron. Environmental Science and Technology, 36(10), pp. 2178–2184. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es011474g DOI: 10.1021/es011474g]</ref><ref name="Amezquita-Garcia2013">Amezquita-Garcia, H.J., Razo-Flores, E., Cervantes, F.J., and Rangel-Mendez, J.R., 2013. Activated carbon fibers as redox mediators for the increased reduction of nitroaromatics. Carbon, 55, pp. 276–284. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2012.12.062 DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2012.12.062]</ref><ref name="Xin2022">Xin, D., Girón, J., Fuller, M.E., and Chiu, P.C., 2022. Abiotic Reduction of 3-Nitro-1,2,4-triazol-5-one (NTO) and Other Munitions Constituents by Wood-Derived Biochar through Its Rechargeable Electron Storage Capacity. Environmental Science: Processes and Impacts, 24(2), pp. 316-329. [https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00447F DOI: 10.1039/D1EM00447F]</ref>, and sulfides<ref name="Hojo1960">Hojo, M., Takagi, Y. and Ogata, Y., 1960. Kinetics of the Reduction of Nitrobenzenes by Sodium Disulfide. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 82(10), pp. 2459–2462. [https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01495a017 DOI: 10.1021/ja01495a017]</ref><ref name="Zeng2012">Zeng, T., Chin, Y.P., and Arnold, W.A., 2012. Potential for Abiotic Reduction of Pesticides in Prairie Pothole Porewaters. Environmental Science and Technology, 46(6), pp. 3177–3187. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es203584d DOI: 10.1021/es203584d]</ref>. These geo-reductants may control the fate and half-lives of MCs in the environment and can be used to promote MC degradation in soil and groundwater through enhanced natural attenuation<ref name="USEPA2012">US EPA, 2012. A Citizen’s Guide to Monitored Natural Attenuation. EPA document 542-F-12-014. [https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-04/documents/a_citizens_guide_to_monitored_natural_attenuation.pdf Free download.]</ref>.
| + | |
| | + | [[File:StrathmannFig2.png | thumb | 300px| Figure 2. Effect of perfluoroalkyl carbon chain length on the estimated bed volumes (BVs) to 50% breakthrough of PFCAs and PFSAs observed in a pilot study<ref name="StrathmannEtAl2020">Strathmann, T.J., Higgins, C., Deeb, R., 2020. Hydrothermal Technologies for On-Site Destruction of Site Investigation Wastes Impacted by PFAS, Final Report - Phase I. SERDP Project ER18-1501. [https://serdp-estcp.mil/projects/details/b34d6396-6b6d-44d0-a89e-6b22522e6e9c Project Website] [[Media: ER18-1501.pdf | Report.pdf]]</ref> treating PFAS-contaminated groundwater with the PFAS-selective AER (Purolite PFA694E) ]] |
| | | | |
| − | [[File:AbioMCredFig2.png | thumb |450px|Figure 2. General mechanism for the reduction of NACs/MCs.]] | + | Anion exchange is an adsorptive treatment technology that uses polymeric resin beads (0.5–1 mm diameter) that incorporate cationic adsorption sites to remove anionic pollutants from water<ref>SenGupta, A.K., 2017. Ion Exchange in Environmental Processes: Fundamentals, Applications and Sustainable Technology. Wiley. ISBN:9781119157397 [https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/book/10.1002/9781119421252 Wiley Online Library]</ref>. Anions (e.g., NO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup>) are adsorbed by an ion exchange reaction with anions that are initially bound to the adsorption sites (e.g., Cl<sup>-</sup>) during resin preparation. Many per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) of concern, including [[Wikipedia: Perfluorooctanoic acid | perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA)]] and [[Wikipedia: Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid | perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS)]], are present in contaminated water as anionic species that can be adsorbed by anion exchange reactions<ref name="BoyerEtAl2021a"/><ref name="DixitEtAl2021">Dixit, F., Dutta, R., Barbeau, B., Berube, P., Mohseni, M., 2021. PFAS Removal by Ion Exchange Resins: A Review. Chemosphere, 272, Article 129777. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129777 doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129777]</ref><ref name="RahmanEtAl2014">Rahman, M.F., Peldszus, S., Anderson, W.B., 2014. Behaviour and Fate of Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Drinking Water Treatment: A Review. Water Research, 50, pp. 318–340. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.10.045 doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2013.10.045]</ref>. |
| − | [[File:AbioMCredFig3.png | thumb |450px|Figure 3. Schematic of natural attenuation of MCs-impacted soils through chemical reduction.]]
| + | </br> |
| − | Although the chemical structures of MCs can vary significantly (Figure 1), most of them contain at least one nitro functional group (-NO<sub>2</sub>), which is susceptible to reductive transformation<ref name="Spain2000">Spain, J.C., Hughes, J.B., and Knackmuss, H.J., 2000. Biodegradation of Nitroaromatic Compounds and Explosives. CRC Press, 456 pages. ISBN: 9780367398491</ref>. Of the MCs shown in Figure 1, 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT), 2,4-dinitroanisole (DNAN), and 3-nitro-1,2,4-triazol-5-one (NTO)<ref name="Harris1996">Harris, N.J., and Lammertsma, K., 1996. Tautomerism, Ionization, and Bond Dissociations of 5-Nitro-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazolone. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 118(34), pp. 8048–8055. [https://doi.org/10.1021/ja960834a DOI: 10.1021/ja960834a]</ref> are nitroaromatic compounds (NACs) and hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) and nitroguanidine (NQ) are nitramines. The structural differences may result in different reactivities and reaction pathways. Reduction of NACs results in the formation of aromatic amines (i.e., anilines) with nitroso and hydroxylamine compounds as intermediates (Figure 2)<ref name="Schwarzenbach2016"/>.
| + | <center><big>Anion Exchange Reaction: '''PFAS<sup>-</sup></big><sub>(aq)</sub><big> + Cl<sup>-</sup></big><sub>(resin bound)</sub><big> ⇒ PFAS<sup>-</sup></big><sub>(resin bound)</sub><big> + Cl<sup>-</sup></big><sub>(aq)</sub>'''</center> |
| | + | Resins most commonly applied for PFAS treatment are strong base anion exchange resins (SB-AERs) that incorporate [[Wikipedia: Quaternary ammonium cation | quaternary ammonium]] cationic functional groups with hydrocarbon side chains (R-groups) that promote PFAS adsorption by a combination of electrostatic and hydrophobic mechanisms (Figure 1)<ref name="BoyerEtAl2021a"/><ref>Fuller, Mark. Ex Situ Treatment of PFAS-Impacted Groundwater Using Ion Exchange with Regeneration; ER18-1027. [https://serdp-estcp.mil/projects/details/af660326-56e0-4d3c-b80a-1d8a2d613724 Project Website].</ref>. SB-AERs maintain cationic functional groups independent of water pH. Recently introduced ‘PFAS-selective’ AERs show >1,000,000-fold greater selectivity for some PFAS over the Cl<sup>-</sup> initially loaded onto resins<ref name="FangEtAl2021">Fang, Y., Ellis, A., Choi, Y.J., Boyer, T.H., Higgins, C.P., Schaefer, C.E., Strathmann, T.J., 2021. Removal of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Aqueous Film-Forming Foam (AFFF) Using Ion-Exchange and Nonionic Resins. Environmental Science and Technology, 55(8), pp. 5001–5011. [https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c00769 doi: 10.1021/acs.est.1c00769]</ref>. These resins also show much higher adsorption capacities for PFAS (mg PFAS adsorbed per gram of adsorbent media) than granular activated carbon (GAC) adsorbents. |
| | | | |
| − | Although the final reduction products are different for non-aromatic MCs, the reduction process often starts with the transformation of the -NO<sub>2</sub> moiety, either through de-nitration (e.g., RDX<ref name="Kwon2008">Kwon, M.J., and Finneran, K.T., 2008. Biotransformation products and mineralization potential for hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) in abiotic versus biological degradation pathways with anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate (AQDS) and ''Geobacter metallireducens''. Biodegradation, 19(5), pp. 705–715. [https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-008-9175-5 DOI: 10.1007/s10532-008-9175-5]</ref><ref name="Halasz2011">Halasz, A., and Hawari, J., 2011. Degradation Routes of RDX in Various Redox Systems. Aquatic Redox Chemistry, American Chemical Society, 1071(20), pp. 441-462. [https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-2011-1071.ch020 DOI: 10.1021/bk-2011-1071.ch020]</ref>) or reduction to nitroso<ref name="Kwon2006"/><ref name="Tong2021">Tong, Y., Berens, M.J., Ulrich, B.A., Bolotin, J., Strehlau, J.H., Hofstetter, T.B., and Arnold, W.A., 2021. Exploring the Utility of Compound-Specific Isotope Analysis for Assessing Ferrous Iron-Mediated Reduction of RDX in the Subsurface. Environmental Science and Technology, 55(10), pp. 6752–6763. [https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c08420 DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.0c08420]</ref> followed by ring cleavage<ref name="Kim2007"/><ref name="Halasz2011"/><ref name="Tong2021"/><ref name="Larese-Casanova2008">Larese-Casanova, P., and Scherer, M.M., 2008. Abiotic Transformation of Hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) by Green Rusts. Environmental Science and Technology, 42(11), pp. 3975–3981. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es702390b DOI: 10.1021/es702390b]</ref>.
| + | PFAS of concern include a wide range of structures, including [[Wikipedia: Perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids | perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids (PFCAs)]] and [[Wikipedia: Perfluorosulfonic acids | perfluoroalkyl sulfonic acids (PFSAs)]] of varying carbon chain length<ref>Interstate Technology Regulatory Council (ITRC), 2023. Technical Resources for Addressing Environmental Releases of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS). [https://pfas-1.itrcweb.org/ ITRC PFAS Website]</ref>. As such, affinity for adsorption to AERs is heavily dependent upon PFAS structure<ref name="BoyerEtAl2021a"/><ref name="DixitEtAl2021"/>. In general, it has been found that the extent of adsorption increases with increasing chain length, and that PFSAs adsorb more strongly than PFCAs of similar chain length (Figure 2)<ref name="FangEtAl2021"/><ref>Gagliano, E., Sgroi, M., Falciglia, P.P., Vagliasindi, F.G.A., Roccaro, P., 2020. Removal of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) from Water by Adsorption: Role of PFAS Chain Length, Effect of Organic Matter and Challenges in Adsorbent Regeneration. Water Research, 171, Article 115381. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.115381 doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.115381]</ref>. The chain length-dependence supports the conclusion that PFAS-resin hydrophobic mechanisms contribute to adsorption. Adsorption of polyfluorinated structures also depend on structure and prevailing charge, with adsorption of zwitterionic species (containing both anionic and cationic groups in the same structure) to AERs being documented despite having a net neutral charge<ref name="FangEtAl2021"/>. |
| | | | |
| − | Figure 3 illustrates a typical MC reduction reaction. A redox-active soil constituent, such as organic matter or iron mineral, donates electrons to an MC and transforms the nitro group into an amino group (R-NH<sub>2</sub>). The rate at which an MC is reduced can vary by many orders of magnitude depending on the soil constituent, the MC, the reduction potential (''E<sub>H</sub>'') and other media conditions<ref name="Borch2010">Borch, T., Kretzschmar, R., Kappler, A., Cappellen, P.V., Ginder-Vogel, M., Voegelin, A., and Campbell, K., 2010. Biogeochemical Redox Processes and their Impact on Contaminant Dynamics. Environmental Science and Technology, 44(1), pp. 15–23. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es9026248 DOI: 10.1021/es9026248] [https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/es9026248 Open access article.]</ref>. | + | ==Reactors for Treatment of PFAS-Contaminated Water== |
| | + | Anion exchange treatment of water is accomplished by pumping contaminated water through fixed bed reactors filled with AERs (Figure 3). A common configuration involves flowing water through two reactors arranged in a lead-lag configuration<ref name="WoodardEtAl2017">Woodard, S., Berry, J., Newman, B., 2017. Ion Exchange Resin for PFAS Removal and Pilot Test Comparison to GAC. Remediation, 27(3), pp. 19–27. [https://doi.org/10.1002/rem.21515 doi: 10.1002/rem.21515]</ref>. Water flows through the pore spaces in close contact with resin beads. Sufficient contact time needs to be provided, referred to as empty bed contact time (EBCT), to allow PFAS to diffuse from the water into the resin structure and adsorb to exchange sites. Typical EBCTs for AER treatment of PFAS are 2-5 min, shorter than contact times recommended for granular activated carbon (GAC) adsorbents (≥10 min)<ref name="LiuEtAl2022">Liu, C. J., Murray, C.C., Marshall, R.E., Strathmann, T.J., Bellona, C., 2022. Removal of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances from Contaminated Groundwater by Granular Activated Carbon and Anion Exchange Resins: A Pilot-Scale Comparative Assessment. Environmental Science: Water Research and Technology, 8(10), pp. 2245–2253. [https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EW00080F doi: 10.1039/D2EW00080F]</ref><ref>Liu, C.J., Werner, D., Bellona, C., 2019. Removal of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) from Contaminated Groundwater Using Granular Activated Carbon: A Pilot-Scale Study with Breakthrough Modeling. Environmental Science: Water Research and Technology, 5(11), pp. 1844–1853. [https://doi.org/10.1039/C9EW00349E doi: 10.1039/C9EW00349E]</ref>. The higher adsorption capacities and shorter EBCTs of AERs enable use of much less media and smaller vessels than GAC, reducing expected capital costs for AER treatment systems<ref name="EllisEtAl2023">Ellis, A.C., Boyer, T.H., Fang, Y., Liu, C.J., Strathmann, T.J., 2023. Life Cycle Assessment and Life Cycle Cost Analysis of Anion Exchange and Granular Activated Carbon Systems for Remediation of Groundwater Contaminated by Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs). Water Research, 243, Article 120324. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2023.120324 doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2023.120324]</ref>. |
| | | | |
| − | The most prevalent reductants in soils are iron minerals and organic carbon such as that found in natural organic matter. It has been suggested that Fe(II)<sub>aq</sub> and dissolved organic matter concentrations could serve as indicators of NAC reducibility in anaerobic sediments<ref name="Zhang2009">Zhang, H., and Weber, E.J., 2009. Elucidating the Role of Electron Shuttles in Reductive Transformations in Anaerobic Sediments. Environmental Science and Technology, 43(4), pp. 1042–1048. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es8017072 DOI: 10.1021/es8017072]</ref>. The following sections summarize these two classes of reductants separately and present advances in our understanding of the kinetics of NAC/MC reduction by these geo-reductants.
| + | Like other adsorption media, PFAS will initially adsorb to media encountered near the inlet side of the reactor, but as ion exchange sites become saturated with PFAS, the active zone of adsorption will begin to migrate through the packed bed with increasing volume of water treated. Moreover, some PFAS with lower affinity for exchange sites (e.g., shorter-chain PFAS that are less hydrophobic) will be displaced by competition from other PFAS (e.g., longer-chain PFAS that are more hydrophobic) and move further along the bed to occupy open sites<ref name="EllisEtAl2022">Ellis, A.C., Liu, C.J., Fang, Y., Boyer, T.H., Schaefer, C.E., Higgins, C.P., Strathmann, T.J., 2022. Pilot Study Comparison of Regenerable and Emerging Single-Use Anion Exchange Resins for Treatment of Groundwater Contaminated by per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs). Water Research, 223, Article 119019. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.119019 doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2022.119019] [[Media: EllisEtAl2022.pdf | Open Access Manuscript]]</ref>. Eventually, PFAS will start to breakthrough into the effluent from the reactor, typically beginning with the shorter-chain compounds. The initial breakthrough of shorter-chain PFAS is similar to the behavior observed for AER treatment of inorganic contaminants. |
| | | | |
| − | ==Carbonaceous Reductants==
| + | Upon breakthrough, treatment is halted, and the exhausted resins are either replaced with fresh media or regenerated before continuing treatment. Most vendors are currently operating AER treatment systems for PFAS in single-use mode where virgin media is delivered to replace exhausted resins, which are transported off-site for disposal or incineration<ref name="BoyerEtAl2021a"/>. As an alternative, some providers are developing regenerable AER treatment systems, where exhausted resins are regenerated on-site by desorbing PFAS from the resins using a combination of salt brine (typically ≥1 wt% NaCl) and cosolvent (typically ≥70 vol% methanol)<ref name="BoyerEtAl2021a"/><ref name="BoyerEtAl2021b">Boyer, T.H., Ellis, A., Fang, Y., Schaefer, C.E., Higgins, C.P., Strathmann, T.J., 2021. Life Cycle Environmental Impacts of Regeneration Options for Anion Exchange Resin Remediation of PFAS Impacted Water. Water Research, 207, Article 117798. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.117798 doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117798] [[Media: BoyerEtAl2021b.pdf | Open Access Manuscript]]</ref><ref>Houtz, E., (projected completion 2025). Treatment of PFAS in Groundwater with Regenerable Anion Exchange Resin as a Bridge to PFAS Destruction, Project ER23-8391. [https://serdp-estcp.mil/projects/details/a12b603d-0d4a-4473-bf5b-069313a348ba/treatment-of-pfas-in-groundwater-with-regenerable-anion-exchange-resin-as-a-bridge-to-pfas-destruction Project Website].</ref>. This mode of operation allows for longer term use of resins before replacement, but requires more complex and extensive site infrastructure. Cosolvent in the resulting waste regenerant can be recycled by distillation, which reduces chemical inputs and lowers the volume of PFAS-contaminated still bottoms requiring further treatment or disposal<ref name="BoyerEtAl2021b"/>. Currently, there is active research on various technologies for destruction of PFAS concentrates in AER still bottoms residuals<ref name="StrathmannEtAl2020">Strathmann, T.J., Higgins, C., Deeb, R., 2020. Hydrothermal Technologies for On-Site Destruction of Site Investigation Wastes Impacted by PFAS, Final Report - Phase I. SERDP Project ER18-1501. [https://serdp-estcp.mil/projects/details/b34d6396-6b6d-44d0-a89e-6b22522e6e9c Project Website] [[Media: ER18-1501.pdf | Report.pdf]]</ref><ref name="HuangEtAl2021">Huang, Q., Woodard, S., Nickleson, M., Chiang, D., Liang, S., Mora, R., 2021. Electrochemical Oxidation of Perfluoroalkyl Acids in Still Bottoms from Regeneration of Ion Exchange Resins Phase I - Final Report. SERDP Project ER18-1320. [https://serdp-estcp.mil/projects/details/ccaa70c4-b40a-4520-ba17-14db2cd98e8f Project Website] [[Media: ER18-1320.pdf | Report.pdf]]</ref>. |
| − | [[File:AbioMCredFig4.png | thumb |600px|Figure 4. Chemical structure of commonly used hydroquinones in NACs/MCs kinetic experiments.]]
| |
| − | The two most predominant forms of organic carbon in natural systems are natural organic matter (NOM) and black carbon (BC)<ref name="Schumacher2002">Schumacher, B.A., 2002. Methods for the Determination of Total Organic Carbon (TOC) in Soils and Sediments. U.S. EPA, Ecological Risk Assessment Support Center. [http://bcodata.whoi.edu/LaurentianGreatLakes_Chemistry/bs116.pdf Free download.]</ref>. Black carbon includes charcoal, soot, graphite, and coal. Until the early 2000s black carbon was considered to be a class of (bio)chemically inert geosorbents<ref name="Schmidt2000">Schmidt, M.W.I., and Noack, A.G., 2000. Black carbon in soils and sediments: Analysis, distribution, implications, and current challenges. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 14(3), pp. 777–793. [https://doi.org/10.1029/1999GB001208 DOI: 10.1029/1999GB001208] [https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1029/1999GB001208 Open access article.]</ref>. However, it has been shown that BC can contain abundant quinone functional groups and thus can store and exchange electrons<ref name="Klüpfel2014">Klüpfel, L., Keiluweit, M., Kleber, M., and Sander, M., 2014. Redox Properties of Plant Biomass-Derived Black Carbon (Biochar). Environmental Science and Technology, 48(10), pp. 5601–5611. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es500906d DOI: 10.1021/es500906d]</ref> with chemical<ref name="Xin2019">Xin, D., Xian, M., and Chiu, P.C., 2019. New methods for assessing electron storage capacity and redox reversibility of biochar. Chemosphere, 215, 827–834. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.080 DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.080]</ref> and biological<ref name="Saquing2016">Saquing, J.M., Yu, Y.-H., and Chiu, P.C., 2016. Wood-Derived Black Carbon (Biochar) as a Microbial Electron Donor and Acceptor. Environmental Science and Technology Letters, 3(2), pp. 62–66. [https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.5b00354 DOI: 10.1021/acs.estlett.5b00354]</ref> agents in the surroundings. Specifically, BC such as biochar has been shown to reductively transform MCs including NTO, DNAN, and RDX<ref name="Xin2022"/>.
| |
| | | | |
| − | NOM encompasses all the organic compounds present in terrestrial and aquatic environments and can be classified into two groups, non-humic and humic substances. Humic substances (HS) contain a wide array of functional groups including carboxyl, enol, ether, ketone, ester, amide, (hydro)quinone, and phenol<ref name="Sparks2003">Sparks, D.L., 2003. Environmental Soil Chemistry, 2nd Edition. Elsevier Science and Technology Books. [https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-656446-4.X5000-2 DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-656446-4.X5000-2]</ref>. Quinone and hydroquinone groups are believed to be the predominant redox moieties responsible for the capacity of HS and BC to store and reversibly accept and donate electrons (i.e., through reduction and oxidation of HS/BC, respectively)<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/><ref name="Dunnivant1992"/><ref name="Klüpfel2014"/><ref name="Scott1998">Scott, D.T., McKnight, D.M., Blunt-Harris, E.L., Kolesar, S.E., and Lovley, D.R., 1998. Quinone Moieties Act as Electron Acceptors in the Reduction of Humic Substances by Humics-Reducing Microorganisms. Environmental Science and Technology, 32(19), pp. 2984–2989. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es980272q DOI: 10.1021/es980272q]</ref><ref name="Cory2005">Cory, R.M., and McKnight, D.M., 2005. Fluorescence Spectroscopy Reveals Ubiquitous Presence of Oxidized and Reduced Quinones in Dissolved Organic Matter. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(21), pp 8142–8149. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es0506962 DOI: 10.1021/es0506962]</ref><ref name="Fimmen2007">Fimmen, R.L., Cory, R.M., Chin, Y.P., Trouts, T.D., and McKnight, D.M., 2007. Probing the oxidation–reduction properties of terrestrially and microbially derived dissolved organic matter. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(12), pp. 3003–3015. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2007.04.009 DOI: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.04.009]</ref><ref name="Struyk2001">Struyk, Z., and Sposito, G., 2001. Redox properties of standard humic acids. Geoderma, 102(3-4), pp. 329–346. [https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7061(01)00040-4 DOI: 10.1016/S0016-7061(01)00040-4]</ref><ref name="Ratasuk2007">Ratasuk, N., and Nanny, M.A., 2007. Characterization and Quantification of Reversible Redox Sites in Humic Substances. Environmental Science and Technology, 41(22), pp. 7844–7850. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es071389u DOI: 10.1021/es071389u]</ref><ref name="Aeschbacher2010">Aeschbacher, M., Sander, M., and Schwarzenbach, R.P., 2010. Novel Electrochemical Approach to Assess the Redox Properties of Humic Substances. Environmental Science and Technology, 44(1), pp. 87–93. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es902627p DOI: 10.1021/es902627p]</ref><ref name="Aeschbacher2011">Aeschbacher, M., Vergari, D., Schwarzenbach, R.P., and Sander, M., 2011. Electrochemical Analysis of Proton and Electron Transfer Equilibria of the Reducible Moieties in Humic Acids. Environmental Science and Technology, 45(19), pp. 8385–8394. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es201981g DOI: 10.1021/es201981g]</ref><ref name="Bauer2009">Bauer, I., and Kappler, A., 2009. Rates and Extent of Reduction of Fe(III) Compounds and O<sub>2</sub> by Humic Substances. Environmental Science and Technology, 43(13), pp. 4902–4908. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es900179s DOI: 10.1021/es900179s]</ref><ref name="Maurer2010">Maurer, F., Christl, I. and Kretzschmar, R., 2010. Reduction and Reoxidation of Humic Acid: Influence on Spectroscopic Properties and Proton Binding. Environmental Science and Technology, 44(15), pp. 5787–5792. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es100594t DOI: 10.1021/es100594t]</ref><ref name="Walpen2016">Walpen, N., Schroth, M.H., and Sander, M., 2016. Quantification of Phenolic Antioxidant Moieties in Dissolved Organic Matter by Flow-Injection Analysis with Electrochemical Detection. Environmental Science and Technology, 50(12), pp. 6423–6432. [https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b01120 DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.6b01120] [https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/acs.est.6b01120 Open access article.]</ref><ref name="Aeschbacher2012">Aeschbacher, M., Graf, C., Schwarzenbach, R.P., and Sander, M., 2012. Antioxidant Properties of Humic Substances. Environmental Science and Technology, 46(9), pp. 4916–4925. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es300039h DOI: 10.1021/es300039h]</ref><ref name="Nurmi2002">Nurmi, J.T., and Tratnyek, P.G., 2002. Electrochemical Properties of Natural Organic Matter (NOM), Fractions of NOM, and Model Biogeochemical Electron Shuttles. Environmental Science and Technology, 36(4), pp. 617–624. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es0110731 DOI: 10.1021/es0110731]</ref>.
| + | ==Field Demonstrations== |
| | + | Field pilot studies are critical to demonstrating the effectiveness and expected costs of PFAS treatment technologies. A growing number of pilot studies testing the performance of commercially available AERs to treat PFAS-contaminated groundwater, including sites impacted by historical use of aqueous film-forming foam (AFFF), have been published recently (Figure 4) |
| | | | |
| − | Hydroquinones have been widely used as surrogates to understand the reductive transformation of NACs and MCs by NOM. Figure 4 shows the chemical structures of the singly deprotonated forms of four hydroquinone species previously used to study NAC/MC reduction. The second-order rate constants (''k<sub>R</sub>'') for the reduction of NACs/MCs by these hydroquinone species are listed in Table 1, along with the aqueous-phase one electron reduction potentials of the NACs/MCs (''E<sub>H</sub><sup>1’</sup>'') where available. ''E<sub>H</sub><sup>1’</sup>'' is an experimentally measurable thermodynamic property that reflects the propensity of a given NAC/MC to accept an electron in water (''E<sub>H</sub><sup>1</sup>''(R-NO<sub>2</sub>)):
| |
| | | | |
| − | :::::<big>'''Equation 1:''' ''R-NO<sub>2</sub> + e<sup>-</sup> ⇔ R-NO<sub>2</sub><sup>•-</sup>''</big>
| |
| | | | |
| − | Knowing the identity of and reaction order in the reductant is required to derive the second-order rate constants listed in Table 1. This same reason limits the utility of reduction rate constants measured with complex carbonaceous reductants such as NOM<ref name="Dunnivant1992"/>, BC<ref name="Oh2013"/><ref name="Oh2009"/><ref name="Xu2015"/><ref name="Xin2021">Xin, D., 2021. Understanding the Electron Storage Capacity of Pyrogenic Black Carbon: Origin, Redox Reversibility, Spatial Distribution, and Environmental Applications. Doctoral Thesis, University of Delaware. [https://udspace.udel.edu/bitstream/handle/19716/30105/Xin_udel_0060D_14728.pdf?sequence=1 Free download.]</ref>, and HS<ref name="Luan2010"/><ref name="Murillo-Gelvez2021"/>, whose chemical structures and redox moieties responsible for the reduction, as well as their abundance, are not clearly defined or known. In other words, the observed rate constants in those studies are specific to the experimental conditions (e.g., pH and NOM source and concentration), and may not be easily comparable to other studies.
| + | In comparison to other reported PFAS destruction techniques, PRD offers several advantages: |
| | + | *Relative to UV/sodium sulfite and UV/sodium iodide systems, the fitted degradation rates in the micelle-accelerated PRD reaction system were ~18 and ~36 times higher, indicating the key role of the self-assembled micelle in creating a confined space for rapid PFAS destruction<ref name="ChenEtAl2020"/>. The negatively charged hydrated electron associated with the positively charged cetyltrimethylammonium ion (CTA<sup>+</sup>) forms the surfactant micelle to trap molecules with similar structures, selectively mineralizing compounds with both hydrophobic and hydrophilic groups (e.g., PFAS). |
| | + | *The PRD reaction does not require solid catalysts or electrodes, which can be expensive to acquire and difficult to regenerate or dispose. |
| | + | *The aqueous solution is not heated or pressurized, and the UV wavelength used does not cause direct water [[Wikipedia: Photodissociation | photolysis]], therefore the energy input to the system is more directly employed to destroy PFAS, resulting in greater energy efficiency. |
| | + | *Since the reaction is performed at ambient temperature and pressure, there are limited concerns regarding environmental health and safety or volatilization of PFAS compared to heated and pressurized systems. |
| | + | *Due to the reductive nature of the reaction, there is no formation of unwanted byproducts resulting from oxidative processes, such as [[Wikipedia: Perchlorate | perchlorate]] generation during electrochemical oxidation<ref>Veciana, M., Bräunig, J., Farhat, A., Pype, M. L., Freguia, S., Carvalho, G., Keller, J., Ledezma, P., 2022. Electrochemical Oxidation Processes for PFAS Removal from Contaminated Water and Wastewater: Fundamentals, Gaps and Opportunities towards Practical Implementation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 434, Article 128886. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128886 doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128886]</ref><ref>Trojanowicz, M., Bojanowska-Czajka, A., Bartosiewicz, I., Kulisa, K., 2018. Advanced Oxidation/Reduction Processes Treatment for Aqueous Perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) and Perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) – A Review of Recent Advances. Chemical Engineering Journal, 336, pp. 170–199. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.153 doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.153]</ref><ref>Wanninayake, D.M., 2021. Comparison of Currently Available PFAS Remediation Technologies in Water: A Review. Journal of Environmental Management, 283, Article 111977. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.111977 doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.111977]</ref>. |
| | + | *Aqueous fluoride ions are the primary end products of PRD, enabling real-time reaction monitoring with a fluoride [[Wikipedia: Ion-selective electrode | ion selective electrode (ISE)]], which is far less expensive and faster than relying on PFAS analytical data alone to monitor system performance. |
| | | | |
| − | {| class="wikitable mw-collapsible" style="float:left; margin-right:40px; text-align:center;"
| + | ===Disadvantages=== |
| − | |+ Table 1. Aqueous phase one electron reduction potentials and logarithm of second-order rate constants for the reduction of NACs and MCs by the singly deprotonated form of the hydroquinones lawsone, juglone, AHQDS and AHQS, with the second-order rate constants for the deprotonated NAC/MC species (i.e., nitrophenolates and NTO<sup>–</sup>) in parentheses.
| + | *The CTAB additive is only partially consumed during the reaction, and although CTAB is not problematic when discharged to downstream treatment processes that incorporate aerobic digestors, CTAB can be toxic to surface waters and anaerobic digestors. Therefore, disposal options for treated solutions will need to be evaluated on a site-specific basis. Possible options include removal of CTAB from solution for reuse in subsequent PRD treatments, or implementation of an oxidation reaction to degrade CTAB. |
| − | |-
| + | *The PRD reaction rate decreases in water matrices with high levels of total dissolved solids (TDS). It is hypothesized that in high TDS solutions (e.g., ion exchange still bottoms with TDS of 200,000 ppm), the presence of ionic species inhibits the association of the electron donor with the micelle, thus decreasing the reaction rate. |
| − | ! Compound
| + | *The PRD reaction rate decreases in water matrices with very low UV transmissivity. Low UV transmissivity (i.e., < 1 %) prevents the penetration of UV light into the solution, such that the utilization efficiency of UV light decreases. |
| − | ! rowspan="2" |''E<sub>H</sub><sup>1'</sup>'' (V)
| |
| − | ! colspan="4"| Hydroquinone (log ''k<sub>R</sub>'' (M<sup>-1</sup>s<sup>-1</sup>))
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! (NAC/MC)
| |
| − | ! LAW<sup>-</sup>
| |
| − | ! JUG<sup>-</sup>
| |
| − | ! AHQDS<sup>-</sup>
| |
| − | ! AHQS<sup>-</sup>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | Nitrobenzene (NB) || -0.485<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || 0.380<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || -1.102<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || 2.050<ref name="Murillo-Gelvez2019"/> || 3.060<ref name="Murillo-Gelvez2019"/>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 2-nitrotoluene (2-NT) || -0.590<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || -1.432<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || -2.523<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || 0.775<ref name="Hartenbach2008"/> ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 3-nitrotoluene (3-NT) || -0.475<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || 0.462<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || -0.921<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-nitrotoluene (4-NT) || -0.500<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || 0.041<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || -1.292<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || 1.822<ref name="Hartenbach2008"/> || 2.610<ref name="Murillo-Gelvez2019"/>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 2-chloronitrobenzene (2-ClNB) || -0.485<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || 0.342<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || -0.824<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> ||2.412<ref name="Hartenbach2008"/> ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 3-chloronitrobenzene (3-ClNB) || -0.405<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || 1.491<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || 0.114<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-chloronitrobenzene (4-ClNB) || -0.450<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || 1.041<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || -0.301<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || 2.988<ref name="Hartenbach2008"/> ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 2-acetylnitrobenzene (2-AcNB) || -0.470<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || 0.519<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || -0.456<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 3-acetylnitrobenzene (3-AcNB) || -0.405<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || 1.663<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || 0.398<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-acetylnitrobenzene (4-AcNB) || -0.360<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || 2.519<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || 1.477<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 2-nitrophenol (2-NP) || || 0.568 (0.079)<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) || || -0.699 (-1.301)<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-methyl-2-nitrophenol (4-Me-2-NP) || || 0.748 (0.176)<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol (4-Cl-2-NP) || || 1.602 (1.114)<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 5-fluoro-2-nitrophenol (5-Cl-2-NP) || || 0.447 (-0.155)<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/> || || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) || -0.280<ref name="Schwarzenbach2016"/> || || 2.869<ref name="Hofstetter1999"/> || 5.204<ref name="Hartenbach2008"/> ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 2-amino-4,6-dinitrotoluene (2-A-4,6-DNT) || -0.400<ref name="Schwarzenbach2016"/> || || 0.987<ref name="Hofstetter1999"/> || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-amino-2,6-dinitrotoluene (4-A-2,6-DNT) || -0.440<ref name="Schwarzenbach2016"/> || || 0.079<ref name="Hofstetter1999"/> || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 2,4-diamino-6-nitrotoluene (2,4-DA-6-NT) || -0.505<ref name="Schwarzenbach2016"/> || || -1.678<ref name="Hofstetter1999"/> || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 2,6-diamino-4-nitrotoluene (2,6-DA-4-NT) || -0.495<ref name="Schwarzenbach2016"/> || || -1.252<ref name="Hofstetter1999"/> || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 1,3-dinitrobenzene (1,3-DNB) || -0.345<ref name="Hofstetter1999"/> || || 1.785<ref name="Hofstetter1999"/> || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 1,4-dinitrobenzene (1,4-DNB) || -0.257<ref name="Hofstetter1999"/> || || 3.839<ref name="Hofstetter1999"/> || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 2-nitroaniline (2-NANE) || < -0.560<ref name="Hofstetter1999"/> || || -2.638<ref name="Hofstetter1999"/> || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 3-nitroaniline (3-NANE) || -0.500<ref name="Hofstetter1999"/> || || -1.367<ref name="Hofstetter1999"/> || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 1,2-dinitrobenzene (1,2-DNB) || -0.290<ref name="Hofstetter1999"/> || || || 5.407<ref name="Hartenbach2008"/> ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-nitroanisole (4-NAN) || || -0.661<ref name="Murillo-Gelvez2019"/> || || 1.220<ref name="Murillo-Gelvez2019"/> ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 2-amino-4-nitroanisole (2-A-4-NAN) || || -0.924<ref name="Murillo-Gelvez2019"/> || || 1.150<ref name="Murillo-Gelvez2019"/> || 2.190<ref name="Murillo-Gelvez2019"/>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-amino-2-nitroanisole (4-A-2-NAN) || || || ||1.610<ref name="Murillo-Gelvez2019"/> || 2.360<ref name="Murillo-Gelvez2019"/>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 2-chloro-4-nitroaniline (2-Cl-5-NANE) || || -0.863<ref name="Murillo-Gelvez2019"/> || || 1.250<ref name="Murillo-Gelvez2019"/> || 2.210<ref name="Murillo-Gelvez2019"/>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | N-methyl-4-nitroaniline (MNA) || || -1.740<ref name="Murillo-Gelvez2019"/> || || -0.260<ref name="Murillo-Gelvez2019"/> || 0.692<ref name="Murillo-Gelvez2019"/>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 3-nitro-1,2,4-triazol-5-one (NTO) || || || || 5.701 (1.914)<ref name="Murillo-Gelvez2021"/> ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | Hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) || || || || -0.349<ref name="Kwon2008"/> ||
| |
| − | |}
| |
| | | | |
| − | [[File:AbioMCredFig5.png | thumb |500px|Figure 5. Relative reduction rate constants of the NACs/MCs listed in Table 1 for AHQDS<sup>–</sup>. Rate constants are compared with respect to RDX. Abbreviations of NACs/MCs as listed in Table 1.]]
| + | ==State of the Art== |
| − | Most of the current knowledge about MC degradation is derived from studies using NACs. The reduction kinetics of only four MCs, namely TNT, N-methyl-4-nitroaniline (MNA), NTO, and RDX, have been investigated with hydroquinones. Of these four MCs, only the reduction rates of MNA and TNT have been modeled<ref name="Hofstetter1999"/><ref name="Murillo-Gelvez2019"/><ref name="Riefler2000">Riefler, R.G., and Smets, B.F., 2000. Enzymatic Reduction of 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene and Related Nitroarenes: Kinetics Linked to One-Electron Redox Potentials. Environmental Science and Technology, 34(18), pp. 3900–3906. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es991422f DOI: 10.1021/es991422f]</ref><ref name="Salter-Blanc2015">Salter-Blanc, A.J., Bylaska, E.J., Johnston, H.J., and Tratnyek, P.G., 2015. Predicting Reduction Rates of Energetic Nitroaromatic Compounds Using Calculated One-Electron Reduction Potentials. Environmental Science and Technology, 49(6), pp. 3778–3786. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es505092s DOI: 10.1021/es505092s] [https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/es505092s Open access article.]</ref>.
| |
| | | | |
| − | Using the rate constants obtained with AHQDS<sup>–</sup>, a relative reactivity trend can be obtained (Figure 5). RDX is the slowest reacting MC in Table 1, hence it was selected to calculate the relative rates of reaction (i.e., log ''k<sub>NAC/MC</sub>'' – log ''k<sub>RDX</sub>''). If only the MCs in Figure 5 are considered, the reactivity spans 6 orders of magnitude following the trend: RDX ≈ MNA < NTO<sup>–</sup> < DNAN < TNT < NTO. The rate constant for DNAN reduction by AHQDS<sup>–</sup> is not yet published and hence not included in Table 1. Note that speciation of NACs/MCs can significantly affect their reduction rates. Upon deprotonation, the NAC/MC becomes negatively charged and less reactive as an oxidant (i.e., less prone to accept an electron). As a result, the second-order rate constant can decrease by 0.5-0.6 log unit in the case of nitrophenols and approximately 4 log units in the case of NTO (numbers in parentheses in Table 1)<ref name="Schwarzenbach1990"/><ref name="Murillo-Gelvez2021"/>.
| + | ===Technical Performance=== |
| | + | [[File:WittFig2.png | thumb |400px| Figure 2. Enspired Solutions<small><sup>TM</sup></small> commercial PRD PFAS destruction equipment, the PFASigator<small><sup>TM</sup></small>. Dimensions are 8 feet long by 4 feet wide by 9 feet tall.]] |
| | | | |
| − | ==Ferruginous Reductants==
| + | {| class="wikitable mw-collapsible" style="float:left; margin-right:20px; text-align:center;" |
| − | {| class="wikitable mw-collapsible" style="float:right; margin-left:40px; text-align:center;" | + | |+Table 1. Percent decreases from initial PFAS concentrations during benchtop testing of PRD treatment in different water matrices |
| − | |+ Table 2. Logarithm of second-order rate constants for reduction of NACs and MCs by dissolved Fe(II) complexes with the stoichiometry of ligand and iron in square brackets | |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | ! Compound | + | ! Analytes |
| − | ! E<sub>H</sub><sup>1'</sup> (V) | + | ! |
| − | ! Cysteine</br>[FeL<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2-</sup> | + | ! GW |
| − | ! Thioglycolic acid</br>[FeL<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2-</sup> | + | ! FF |
| − | ! DFOB</br>[FeHL]<sup>0</sup> | + | ! AFFF<br>Rinsate |
| − | ! AcHA</br>[FeL<sub>3</sub>]<sup>-</sup> | + | ! AFF<br>(diluted 10X) |
| − | ! Tiron</br>[FeL<sub>2</sub>]<sup>6-</sup>
| + | ! IDW NF |
| − | ! Fe-Porphyrin | |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | Nitrobenzene || -0.485 j || -0.347 || 0.874 || 2.235 || -0.136 || 1.424 d/</br>4.000 e || -0.018 h</br>0.026 i | + | | Σ Total PFAS<small><sup>a</sup></small> (ND=0) |
| | + | | rowspan="9" style="background-color:white;" | <p style="writing-mode: vertical-rl">% Decrease<br>(Initial Concentration, μg/L)</p> |
| | + | | 93%<br>(370) || 96%<br>(32,000) || 89%<br>(57,000) || 86 %<br>(770,000) || 84%<br>(82) |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | 2-nitrotoluene || -0.590 j || || || || || || -0.602 h | + | | Σ Total PFAS (ND=MDL) || 93%<br>(400) || 86%<br>(32,000) || 90%<br>(59,000) || 71%<br>(770,000) || 88%<br>(110) |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 3-nitrotoluene || -0.475 j || -0.434 || 0.767 || 2.106 || -0.229 || 1.999 d</BR>3.800 e || 0.041 h
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-nitrotoluene || -0.500 j || -0.652 || 0.528 || 2.013 || -0.402 || 1.446 d</br>3.500 e || -0.174 h
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 2-chloronitrobenzene || -0.485 j || || || || || || 0.944 h
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 3-chloronitrobenzene || -0.405 j || 0.360 || 1.810 || 2.888 || 0.691 || 2.882 d</br>4.900 e || 0.724 h
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-chloronitrobenzene || -0.450 j || 0.230 || 1.415 || 2.512 || 0.375 || 3.937 d</br>4.581 e || 0.431 h</br>0.289 i
| |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | 2-acetylnitrobenzene || -0.470 j || || || || || || 1.377 h | + | | Σ Total PFAS (ND=RL) || 94%<br>(460) || 96%<br>(32,000) || 91%<br>(66,000) || 34%<br>(770,000) || 92%<br>(170) |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 3-acetylnitrobenzene || -0.405 j || || || || || || 0.799 h
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-acetylnitrobenzene || -0.360 j || 0.965 || 2.771 || || 1.872 || 5.028 d</br>6.300 e || 1.693 h
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX || -0.550 k || || || || || 2.212 d</br>2.864 f ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | HMX || -0.660 k || || || || || -2.762 d ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | TNT || -0.280 l || || || || || 7.427 d || 2.050 i
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 1,3-dinitrobenzene || -0.345 m || || || || || || 1.220 i
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 2,4-dinitrotoluene || -0.380 n || || || || || 5.319 d || 1.156 i
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | Nitroguanidine (NQ) || -0.700 o || || || || || -0.185 d ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 2,4-dinitroanisole (DNAN) || -0.400 k || || || || || || 1.243 i
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | colspan="8" style="text-align:left; background-color:white;" | Notes:</br>''<sup>a</sup>''
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | {| class="wikitable mw-collapsible" style="float:left; margin-right:40px; text-align:center;"
| |
| − | |+ Table 3. Rate constants for the reduction of MCs by iron minerals
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! MC
| |
| − | ! Iron Mineral
| |
| − | ! Iron mineral loading</br>(g/L)
| |
| − | ! Surface area</br>(m<sup>2</sup>/g)
| |
| − | ! Fe(II)<sub>aq</sub> initial</br>(mM) ''<sup>b</sup>''
| |
| − | ! Fe(II)<sub>aq</sub> after 24 h</br>(mM) ''<sup>c</sup>''
| |
| − | ! Fe(II)<sub>aq</sub> sorbed</br>(mM) ''<sup>d</sup>''
| |
| − | ! pH
| |
| − | ! Buffer
| |
| − | ! Buffer</br>(mM)
| |
| − | ! MC initial</br>(μM) ''<sup>e</sup>''
| |
| − | ! log ''k<sub>obs</sub>''</br>(h<sup>-1</sup>) ''<sup>f</sup>''
| |
| − | ! log ''k<sub>SA</sub>''</br>(Lh<sup>-1</sup>m<sup>-2</sup>) ''<sup>g</sup>''
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | TNT 29 || Goethite || 0.64 || 17.5 || 1.5 || || || 7.0 || MOPS || 25 || 50 || 1.200 || 0.170
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 80 || Magnetite || 1.00 || 44 || 0.1 || 0 || 0.10 || 7.0 || HEPES || 50 || 50 || -3.500 || -5.200
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 80 || Magnetite || 1.00 || 44 || 0.2 || 0.02 || 0.18 || 7.0 || HEPES || 50 || 50 || -2.900 || -4.500
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 80 || Magnetite || 1.00 || 44 || 0.5 || 0.23 || 0.27 || 7.0 || HEPES || 50 || 50 || -1.900 || -3.600
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 80 || Magnetite || 1.00 || 44 || 1.5 || 0.94 || 0.56 || 7.0 || HEPES || 50 || 50 || -1.400 || -3.100
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 80 || Magnetite || 1.00 || 44 || 3.0 || 1.74 || 1.26 || 7.0 || HEPES || 50 || 50 || -1.200 || -2.900
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 80 || Magnetite || 1.00 || 44 || 5.0 || 3.38 || 1.62 || 7.0 || HEPES || 50 || 50 || -1.100 || -2.800
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 80 || Magnetite || 1.00 || 44 || 10.0 || 7.77 || 2.23 || 7.0 || HEPES || 50 || 50 || -1.000 || -2.600
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 80 || Magnetite || 1.00 || 44 || 1.6 || 1.42 || 0.16 || 6.0 || MES || 50 || 50 || -2.700 || -4.300
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 80 || Magnetite || 1.00 || 44 || 1.6 || 1.34 || 0.24 || 6.5 || MOPS || 50 || 50 || -1.800 || -3.400
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 80 || Magnetite || 1.00 || 44 || 1.6 || 1.21 || 0.37 || 7.0 || MOPS || 50 || 50 || -1.200 || -2.900
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 80 || Magnetite || 1.00 || 44 || 1.6 || 1.01 || 0.57 || 7.0 || HEPES || 50 || 50 || -1.200 || -2.800
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 80 || Magnetite || 1.00 || 44 || 1.6 || 0.76 || 0.82 || 7.5 || HEPES || 50 || 50 || -0.490 || -2.100
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 80 || Magnetite || 1.00 || 44 || 1.6 || 0.56 || 1.01 || 8.0 || HEPES || 50 || 50 || -0.590 || -2.200
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NG 82 || Magnetite || 4.00 || 0.56|| 4.0 || || || 7.4 || HEPES || 90 || 226 || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NG 85 || Pyrite || 20.00 || 0.53 || || || || 7.4 || HEPES || 100 || 307 || -2.213 || -3.238
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | TNT 85 || Pyrite || 20.00 || 0.53 || || || || 7.4 || HEPES || 100 || 242 || -2.812 || -3.837
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 85 || Pyrite || 20.00 || 0.53 || || || || 7.4 || HEPES || 100 || 201 || -3.058 || -4.083
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 51 || Carbonate Green Rust || 5.00 || 36 || || || || 7.0 || || || 100 || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 51 || Sulfate Green Rust || 5.00 || 20 || || || || 7.0 || || || 100 || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | DNAN 83 || Sulfate Green Rust || 10.00 || || || || || 8.4 || || || 500 || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NTO 83 || Sulfate Green Rust || 10.00 || || || || || 8.4 || || || 500 || ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | DNAN 81 || Magnetite || 2.00 || 17.8 || 1.0 || || || 7.0 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 10 || 200 || -0.100 || -1.700
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | DNAN 81 || Mackinawite || 1.50 || || || || || 7.0 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 10 || 200 || 0.061 ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | DNAN 81 || Goethite || 1.00 || 103.8 || 1.0 || || || 7.0 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 10 || 200 || 0.410 || -1.600
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 88 || Magnetite || 0.62 || || 1.0 || || || 7.0 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 10 || 17.5 || -1.100 ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 88 || Magnetite || 0.62 || || || || || 7.0 || MOPS || 50 || 17.5 || -0.270 ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 88 || Magnetite || 0.62 || || 1.0 || || || 7.0 || MOPS || 10 || 17.6 || -0.480 ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NTO 89 || Hematite || 1.00 || 5.7 || 1.0 || 0.92 || 0.08 || 5.5 || MES || 50 || 30 || -0.550 || -1.308
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NTO 89 || Hematite || 1.00 || 5.7 || 1.0 || 0.85 || 0.15 || 6.0 || MES || 50 || 30 || 0.619 || -0.140
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NTO 89 || Hematite || 1.00 || 5.7 || 1.0 || 0.9 || 0.10 || 6.5 || MES || 50 || 30 || 1.348 || 0.590
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NTO 89 || Hematite || 1.00 || 5.7 || 1.0 || 0.77 || 0.23 || 7.0 || MOPS || 50 || 30 || 2.167 || 1.408
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NTO 89 || Hematite ''<sup>a</sup>'' || 1.00 || 5.7 || || 1.01 || || 5.5 || MES || 50 || 30 || -1.444 || -2.200
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NTO 89 || Hematite ''<sup>a</sup>'' || 1.00 || 5.7 || || 0.97 || || 6.0 || MES || 50 || 30 || -0.658 || -1.413
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NTO 89 || Hematite ''<sup>a</sup>'' || 1.00 || 5.7 || || 0.87 || || 6.5 || MES || 50 || 30 || 0.068 || -0.688
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NTO 89 || Hematite ''<sup>a</sup>'' || 1.00 || 5.7 || || 0.79 || || 7.0 || MOPS || 50 || 30 || 1.210 || 0.456
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 50 || Mackinawite || 0.45 || || || || || 6.5 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 10 || 250 || -0.092 ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 50 || Mackinawite || 0.45 || || || || || 7.0 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 10 || 250 || 0.009 ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 50 || Mackinawite || 0.45 || || || || || 7.5 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 10 || 250 || 0.158 ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 50 || Green Rust || 5 || || || || || 6.5 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 10 || 250 || -1.301 ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 50 || Green Rust || 5 || || || || || 7.0 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 10 || 250 || -1.097 ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 50 || Green Rust || 5 || || || || || 7.5 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 10 || 250 || -0.745 ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 50 || Goethite || 0.5 || || 1 || 1 || || 6.5 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 10 || 250 || -0.921 ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 50 || Goethite || 0.5 || || 1 || 1 || || 7.0 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 10 || 250 || -0.347 ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 50 || Goethite || 0.5 || || 1 || 1 || || 7.5 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 10 || 250 || 0.009 ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 50 || Hematite || 0.5 || || 1 || 1 || || 6.5 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 10 || 250 || -0.824 ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 50 || Hematite || 0.5 || || 1 || 1 || || 7.0 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 10 || 250 || -0.456 ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 50 || Hematite || 0.5 || || 1 || 1 || || 7.5 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 10 || 250 || -0.237 ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 50 || Magnetite || 2 || || 1 || 1 || || 6.5 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 10 || 250 || -1.523 ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 50 || Magnetite || 2 || || 1 || 1 || || 7.0 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 10 || 250 || -0.824 ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | RDX 50 || Magnetite || 2 || || 1 || 1 || || 7.5 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 10 || 250 || -0.229 ||
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | DNAN 84 || Mackinawite || 4.28 || 0.25 || || || || 6.5 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 8.5 + 20% CO<sub>2</sub>(g) || 400 || 0.836 || 0.806
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | DNAN 84 || Mackinawite || 4.28 || 0.25 || || || || 7.6 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 95.2 + 20% CO<sub>2</sub>(g) || 400 || 0.762 || 0.732
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | DNAN 84 || Commercial FeS || 5.00 || 0.214 || || || || 6.5 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 8.5 + 20% CO<sub>2</sub>(g) || 400 || 0.477 || 0.447
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | DNAN 84 || Commercial FeS || 5.00 || 0.214 || || || || 7.6 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 95.2 + 20% CO<sub>2</sub>(g) || 400 || 0.745 || 0.716
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NTO 84 || Mackinawite || 4.28 || 0.25 || || || || 6.5 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 8.5 + 20% CO<sub>2</sub>(g) || 1000 || 0.663 || 0.633
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NTO 84 || Mackinawite || 4.28 || 0.25 || || || || 7.6 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 95.2 + 20% CO<sub>2</sub>(g) || 1000 || 0.521 || 0.491
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NTO 84 || Commercial FeS || 5.00 || 0.214 || || || || 6.5 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 8.5 + 20% CO<sub>2</sub>(g) || 1000 || 0.492 || 0.462
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NTO 84 || Commercial FeS || 5.00 || 0.214 || || || || 7.6 || NaHCO<sub>3</sub> || 95.2 + 20% CO<sub>2</sub>(g) || 1000 || 0.427 || 0.398
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | colspan="13" style="text-align:left; background-color:white;" | Notes:</br>''<sup>a</sup>'' Dithionite-reduced hematite; experiments conducted in the presence of 1 mM sulfite. ''<sup>b</sup>'' Initial aqueous Fe(II); not added for Fe(II) bearing minerals. ''<sup>c</sup>'' Aqueous Fe(II) after 24h of equilibration. ''<sup>d</sup>'' Difference between b and c. ''<sup>e</sup>'' Initial nominal MC concentration. ''<sup>f</sup>'' Pseudo-first order rate constant. ''<sup>g</sup>'' Surface area normalized rate constant calculated as ''k<sub>Obs</sub>'' '''/''' (surface area concentration) or ''k<sub>Obs</sub>'' '''/''' (surface area × mineral loading).
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | {| class="wikitable mw-collapsible" style="float:right; margin-left:40px; text-align:center;"
| |
| − | |+ Table 4. Rate constants for the reduction of NACs by iron oxides in the presence of aqueous Fe(II)
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! NAC ''<sup>a</sup>''
| |
| − | ! Iron Oxide
| |
| − | ! Iron oxide loading</br>(g/L)
| |
| − | ! Surface area</br>(m<sup>2</sup>/g)
| |
| − | ! Fe(II)<sub>aq</sub> initial</br>(mM) ''<sup>b</sup>''
| |
| − | ! Fe(II)<sub>aq</sub> after 24 h</br>(mM) ''<sup>c</sup>''
| |
| − | ! Fe(II)<sub>aq</sub> sorbed</br>(mM) ''<sup>d</sup>''
| |
| − | ! pH
| |
| − | ! Buffer
| |
| − | ! Buffer</br>(mM)
| |
| − | ! NAC initial</br>(μM) ''<sup>e</sup>''
| |
| − | ! log ''k<sub>obs</sub>''</br>(h<sup>-1</sup>) ''<sup>f</sup>''
| |
| − | ! log ''k<sub>SA</sub>''</br>(Lh<sup>-1</sup>m<sup>-2</sup>) ''<sup>g</sup>''
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 11 || Magnetite || 0.200 || 56.00 || 1.5000 || || || 7.00 || Phosphate || 10 || 50 || 1.05E+00 || 7.75E-04
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-ClNB 11 || Magnetite || 0.200 || 56.00 || 1.5000 || || || 7.00 || Phosphate || 10 || 50 || 1.14E+00 || 8.69E-02
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-ClNB 29 || Goethite || 0.640 || 17.50 || 1.5000 || || || 7.00 || MOPS || 25 || 50 || -1.01E-01 || -1.15E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-ClNB 13 || Goethite || 1.500 || 16.20 || 1.2400 || 0.9600 || 0.2800 || 7.20 || MOPS || 1.2 || 0.5 - 3 || 1.68E+00 || 2.80E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-ClNB 13 || Hematite || 1.800 || 13.70 || 1.0400 || 1.0100 || 0.0300 || 7.20 || MOPS || 1.2 || 0.5 - 3 || -2.32E+00 || -3.72E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-ClNB 13 || Lepidocrocite || 1.400 || 17.60 || 1.1400 || 1.0000 || 0.1400 || 7.20 || MOPS || 1.2 || 0.5 - 3 || 1.51E+00 || 1.20E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Ferrihydrite || 0.004 || 292.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3500 || 0.0300 || 7.97 || HEPES || 25 || 15 || -7.47E-01 || -8.61E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Ferrihydrite || 0.004 || 292.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3700 || 0.0079 || 7.67 || HEPES || 25 || 15 || -1.51E+00 || -1.62E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Ferrihydrite || 0.004 || 292.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3600 || 0.0200 || 7.50 || MOPS || 25 || 15 || -2.15E+00 || -2.26E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Ferrihydrite || 0.004 || 292.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3600 || 0.0120 || 7.28 || MOPS || 25 || 15 || -3.08E+00 || -3.19E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Ferrihydrite || 0.004 || 292.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3700 || 0.0004 || 7.00 || MOPS || 25 || 15 || -3.22E+00 || -3.34E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Ferrihydrite || 0.004 || 292.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3700 || 0.0024 || 6.80 || MOPSO || 25 || 15 || -3.72E+00 || -3.83E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Ferrihydrite || 0.004 || 292.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3700 || 0.0031 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -3.83E+00 || -3.94E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Ferrihydrite || 0.020 || 292.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3700 || 0.0031 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -3.83E+00 || -4.60E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Ferrihydrite || 0.110 || 292.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3700 || 0.0032 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -1.57E+00 || -3.08E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Ferrihydrite || 0.220 || 292.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3700 || 0.0040 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -1.12E+00 || -2.93E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Ferrihydrite || 0.551 || 292.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3700 || 0.0092 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -6.18E-01 || -2.82E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Ferrihydrite || 1.099 || 292.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3500 || 0.0240 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -3.66E-01 || -2.87E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Ferrihydrite || 1.651 || 292.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3400 || 0.0340 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -8.35E-02 || -2.77E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Ferrihydrite || 2.199 || 292.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3300 || 0.0430 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -3.11E-02 || -2.84E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Hematite || 0.038 || 34.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3320 || 0.0430 || 7.97 || HEPES || 25 || 15 || 1.63E+00 || 1.52E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Hematite || 0.038 || 34.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3480 || 0.0270 || 7.67 || HEPES || 25 || 15 || 1.26E+00 || 1.15E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Hematite || 0.038 || 34.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3470 || 0.0280 || 7.50 || MOPS || 25 || 15 || 7.23E-01 || 6.10E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Hematite || 0.038 || 34.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3680 || 0.0066 || 7.28 || MOPS || 25 || 15 || 4.53E-02 || -6.86E-02
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Hematite || 0.038 || 34.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3710 || 0.0043 || 7.00 || MOPS || 25 || 15 || -3.12E-01 || -4.26E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Hematite || 0.038 || 34.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3710 || 0.0042 || 6.80 || MOPSO || 25 || 15 || -7.75E-01 || -8.89E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Hematite || 0.038 || 34.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3680 || 0.0069 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -1.39E+00 || -1.50E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Hematite || 0.038 || 34.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3750 || 0.0003 || 6.10 || MES || 25 || 15 || -2.77E+00 || -2.88E+00
| |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Hematite || 0.016 || 34.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3730 || 0.0024 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -3.20E+00 || -2.95E+00 | + | | Σ Highly Regulated PFAS<small><sup>b</sup></small> (ND=0) || >99%<br>(180) || >99%<br>(20,000) || 95%<br>(20,000) || 92%<br>(390,000) || 95%<br>(50) |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Hematite || 0.024 || 34.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3690 || 0.0064 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -2.74E+00 || -2.66E+00 | + | | Σ Highly Regulated PFAS (ND=MDL) || >99%<br>(180) || 98%<br>(20,000) || 95%<br>(20,000) || 88%<br>(390,000) || 95%<br> (52) |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Hematite || 0.033 || 34.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3680 || 0.0069 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -1.39E+00 || -1.43E+00 | + | | Σ Highly Regulated PFAS (ND=RL) || >99%<br>(190) || 93%<br>(20,000) || 95%<br>(20,000) || 79%<br>(390,000) || 95%<br>(55) |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Hematite || 0.177 || 34.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3640 || 0.0110 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || 3.58E-01 || -4.22E-01 | + | | Σ High Priority PFAS<small><sup>c</sup></small> (ND=0) || 91%<br>(180) || 98%<br>(20,000) || 85%<br>(20,000) || 82%<br>(400,000) || 94%<br>(53) |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Hematite || 0.353 || 34.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3630 || 0.0120 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || 9.97E-01|| -8.27E-02 | + | | Σ High Priority PFAS (ND=MDL) || 91%<br>(190) || 94%<br>(20,000) || 85%<br>(20,000) || 79%<br>(400,000) || 86%<br>(58) |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Hematite || 0.885 || 34.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3480 || 0.0270 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || 1.34E+00 || -1.34E-01 | + | | Σ High Priority PFAS (ND=RL) || 92%<br>(200) || 87%<br>(20,000) || 86%<br>(21,000) || 70%<br>(400,000) || 87%<br>(65) |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Hematite || 1.771 || 34.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3380 || 0.0370 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || 1.78E+00 || 3.59E-03 | + | | Fluorine mass balance<small><sup>d</sup></small> || ||106% || 109% || 110% || 65% || 98% |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Lepidocrocite || 0.027 || 49.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3460 || 0.0290 || 7.97 || HEPES || 25 || 15 || 1.31E+00 || 1.20E+00 | + | | Sorbed organic fluorine<small><sup>e</sup></small> || || 4% || 4% || 33% || N/A || 31% |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Lepidocrocite || 0.027 || 49.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3610 || 0.0140 || 7.67 || HEPES || 25 || 15 || 5.82E-01 || 4.68E-01
| + | | colspan="7" style="background-color:white; text-align:left" | <small>Notes:<br>GW = groundwater<br>GW FF = groundwater foam fractionate<br>AFFF rinsate = rinsate collected from fire system decontamination<br>AFFF (diluted 10x) = 3M Lightwater AFFF diluted 10x<br>IDW NF = investigation derived waste nanofiltrate<br>ND = non-detect<br>MDL = Method Detection Limit<br>RL = Reporting Limit<br><small><sup>a</sup></small>Total PFAS = 40 analytes + unidentified PFCA precursors<br><small><sup>b</sup></small>Highly regulated PFAS = PFNA, PFOA, PFOS, PFHxS, PFBS, HFPO-DA<br><small><sup>c</sup></small>High priority PFAS = PFNA, PFOA, PFHxA, PFBA, PFOS, PFHxS, PFBS, HFPO-DA<br><small><sup>d</sup></small>Ratio of the final to the initial organic fluorine plus inorganic fluoride concentrations<br><small><sup>e</sup></small>Percent of organic fluorine that sorbed to the reactor walls during treatment<br></small> |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Lepidocrocite || 0.027 || 49.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3480 || 0.0270 || 7.50 || MOPS || 25 || 15 || 4.92E-02 || -6.47E-02
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Lepidocrocite || 0.027 || 49.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3640 || 0.0110 || 7.28 || MOPS || 25 || 15 || 1.62E+00 || -4.90E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Lepidocrocite || 0.027 || 49.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3640 || 0.0110 || 7.00 || MOPS || 25 || 15 || -1.25E+00 || -1.36E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Lepidocrocite || 0.027 || 49.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3620 || 0.0130 || 6.80 || MOPSO || 25 || 15 || -1.74E+00 || -1.86E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Lepidocrocite || 0.027 || 49.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3740 || 0.0015 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -2.58E+00 || -2.69E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Lepidocrocite || 0.027 || 49.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3700 || 0.0046 || 6.10 || MES || 25 || 15 || -3.80E+00 || -3.92E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Lepidocrocite || 0.020 || 49.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3740 || 0.0014 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -2.58E+00 || -2.57E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Lepidocrocite || 11.980 || 49.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3620 || 0.0130 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -5.78E-01 || -3.35E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Lepidocrocite || 0.239 || 49.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3530 || 0.0220 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -2.78E-02 || -1.10E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Lepidocrocite || 0.600 || 49.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3190 || 0.0560 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || 3.75E-01 || -1.09E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Lepidocrocite || 1.198 || 49.00 || 0.3750 || 0.2700 || 0.1050 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || 5.05E-01 || -1.26E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Lepidocrocite || 1.798 || 49.00 || 0.3750 || 0.2230 || 0.1520 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || 5.56E-01 || -1.39E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Lepidocrocite || 2.388 || 49.00 || 0.3750 || 0.1820 || 0.1930 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || 5.28E-01 || -1.54E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Goethite || 0.025 || 51.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3440 || 0.0310 || 7.97 || HEPES || 25 || 15 || 9.21E-01 || 8.07E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Goethite || 0.025 || 51.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3660 || 0.0094 || 7.67 || HEPES || 25 || 15 || 3.05E-01 || 1.91E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Goethite || 0.025 || 51.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3570 || 0.0180 || 7.50 || MOPS || 25 || 15 || -9.96E-02 || -2.14E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Goethite || 0.025 || 51.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3640 || 0.0110 || 7.28 || MOPS || 25 || 15 || -8.18E-01 || -9.32E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Goethite || 0.025 || 51.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3670 || 0.0084 || 7.00 || MOPS || 25 || 15 || -1.61E+00 || -1.73E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Goethite || 0.025 || 51.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3750 || 0.0004 || 6.80 || MOPSO || 25 || 15 || -1.82E+00 || -1.93E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Goethite || 0.025 || 51.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3730 || 0.0018 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -2.26E+00 || -2.37E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Goethite || 0.025 || 51.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3670 || 0.0076 || 6.10 || MES || 25 || 15 || -3.56E+00 || -3.67E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Goethite || 0.020 || 51.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3680 || 0.0069 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -2.26E+00 || -2.27E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Goethite || 0.110 || 51.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3660 || 0.0090 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -3.19E-01 || -1.07E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Goethite || 0.220 || 51.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3540 || 0.0210 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || 5.00E-01 || -5.50E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Goethite || 0.551 || 51.00 || 0.3750 || 0.3220 || 0.0530 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || 1.03E+00 || -4.15E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Goethite || 1.100 || 51.00 || 0.3750 || 0.2740 || 0.1010 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || 1.46E+00 || -2.88E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Goethite || 1.651 || 51.00 || 0.3750 || 0.2330 || 0.1420 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || 1.66E+00 || -2.70E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Goethite || 2.196 || 51.00 || 0.3750 || 0.1910 || 0.1840 || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || 1.83E+00 || -2.19E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-CNNB 6 || Goethite || 0.142 || 51.00 || 0.3750 || || || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || 1.99E-01 || -6.61E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-AcNB 6 || Goethite || 0.142 || 51.00 || 0.3750 || || || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -6.85E-02 || -9.28E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-ClNB 6 || Goethite || 0.142 || 51.00 || 0.3750 || || || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -5.47E-01 || -1.41E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-BrNB 6 || Goethite || 0.142 || 51.00 || 0.3750 || || || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -5.73E-01 || -1.43E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 6 || Goethite || 0.142 || 51.00 || 0.3750 || || || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -7.93E-01 || -1.65E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-MeNB 6 || Goethite || 0.142 || 51.00 || 0.3750 || || || 6.60 || MES || 25 || 15 || -9.79E-01 || -1.84E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-ClNB 10 || Goethite || 0.040 || 186.75 || 1.0000 || 0.8050 || 0.1950 || 7.00 || || || || 1.05E+00 || -3.20E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-ClNB 10 || Goethite || 7.516 || 16.10 || 1.0000 || 0.9260 || 0.0740 || 7.00 || || || || 1.14E+00 || 0.00E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-ClNB 10 || Ferrihydrite || 0.111 || 252.60 || 1.0000 || 0.6650 || 0.3350 || 7.00 || || || || 1.05E+00 || -1.56E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-ClNB 10 || Lepidocrocite || 2.384 || 60.40 || 1.0000 || 0.9250 || 0.0750 || 7.00 || || || || 1.14E+00 || -8.60E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-ClNB 9 || Goethite || 10.000 || 14.90 || 1.0000 || || || 7.20 || HEPES || 10 || 10 - 50 || 2.26E+00 || 8.00E-02
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-ClNB 9 || Goethite || 3.000 || 14.90 || 1.0000 || || || 7.20 || HEPES || 10 || 10 - 50 || 2.38E+00 || 7.30E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-ClNB 9 || Lepidocrocite || 2.700 || 16.20 || 1.0000 || || || 7.20 || HEPES || 10 || 10 - 50 || 9.20E-01 || -7.20E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-ClNB 9 || Lepidocrocite || 10.000 || 16.20 || 1.0000 || || || 7.20 || HEPES || 10 || 10 - 50 || 1.03E+00 || -1.18E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-ClNB 12 || Goethite || 0.325 || 140.00 || 1.0000 || || || 7.00 || Bicarbonate || 10 || 100 || 1.14E+00 || -1.79E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | 4-ClNB 12 || Goethite || 0.325 || 140.00 || 1.0000 || || || 6.50 || Bicarbonate || 10 || 100 || 1.11E+00 || -2.10E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 0.500 || 30.70 || 0.1000 || 0.1120 || 0.0090 || 6.00 || MES || 25 || 12 || -1.42E+00 || -2.61E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 0.500 || 30.70 || 0.5000 || 0.5150 || 0.0240 || 6.00 || MES || 25 || 15 || -7.45E-01 || -1.93E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 0.500 || 30.70 || 1.0000 || 1.0280 || 0.0140 || 6.00 || MES || 25 || 19 || -7.45E-01 || -1.93E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 1.000 || 30.70 || 0.1000 || 0.0960 || 0.0260 || 6.00 || MES || 25 || 13 || -1.12E+00 || -2.61E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 1.000 || 30.70 || 0.5000 || 0.4890 || 0.0230 || 6.00 || MES || 25 || 14 || -5.53E-01 || -2.04E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 1.000 || 30.70 || 1.0000 || 0.9870 || 0.0380 || 6.00 || MES || 25 || 19 || -2.52E-01 || -1.74E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 2.000 || 30.70 || 0.1000 || 0.0800 || 0.0490 || 6.00 || MES || 25 || 11 || -8.86E-01 || -2.67E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 2.000 || 30.70 || 0.6000 || 0.4890 || 0.0640 || 6.00 || MES || 25 || 14 || -1.08E-01 || -1.90E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 2.000 || 30.70 || 1.1000 || 0.9870 || 0.0670 || 6.00 || MES || 25 || 14 || 2.30E-01 || -1.56E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 4.000 || 30.70 || 0.1000 || 0.0600 || 0.0650 || 6.00 || MES || 25 || 11 || -8.89E-01 || -2.98E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 4.000 || 30.70 || 0.6000 || 0.3960 || 0.1550 || 6.00 || MES || 25 || 17 || 1.43E-01 || -1.95E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 4.000 || 30.70 || 1.0000 || 0.8360 || 0.1450 || 6.00 || MES || 25 || 16 || 4.80E-01 || -1.61E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 4.000 || 30.70 || 5.6000 || 5.2110 || 0.3790 || 6.00 || MES || 25 || 15 || 1.17E+00 || -9.19E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 1.000 || 30.70 || 0.1000 || 0.0870 || 0.0300 || 6.50 || MES || 25 || 5.5 || -1.74E-01 || -1.66E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 1.000 || 30.70 || 0.5000 || 0.4920 || 0.0300 || 6.50 || MES || 25 || 15 || 3.64E-01 || -1.12E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 1.000 || 30.70 || 1.0000 || 0.9390 || 0.0650 || 6.50 || MES || 25 || 18 || 6.70E-01 || -8.17E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 2.000 || 30.70 || 0.1000 || 0.0490 || 0.0730 || 6.50 || MES || 25 || 5.2 || 3.01E-01 || -1.49E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 2.000 || 30.70 || 0.5000 || 0.4640 || 0.0710 || 6.50 || MES || 25 || 14 || 8.85E-01 || -9.03E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 2.000 || 30.70 || 1.0000 || 0.9130 || 0.1280 || 6.50 || MES || 25 || 16 || 1.12E+00 || -6.64E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 1.000 || 30.70 || 0.1000 || 0.0630 || 0.0480 || 7.00 || MOPS || 25 || 5.3 || 6.12E-01 || -8.75E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 1.000 || 30.70 || 0.5000 || 0.4690 || 0.0520 || 7.00 || MOPS || 25 || 9 || 1.51E+00 || 2.07E-02
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 1.000 || 30.70 || 1.0000 || 0.9360 || 0.1090 || 7.00 || MOPS || 25 || 18 || 1.33E+00 || -1.53E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 2.000 || 30.70 || 0.1000 || 0.0290 || 0.0880 || 7.00 || MOPS || 25 || 12 || 6.85E-01 || -1.10E+00
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | NB 15 || Goethite || 2.000 || 30.70 || 0.5000 || 0.3950 || 0.1450 || 7.00 || MOPS || 25 || 15 || 1.59E+00 || -1.95E-01
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | colspan="13" style="text-align:left; background-color:white;" | Notes:</br>''<sup>a</sup>'' The NACs are Nitrobenzene (NB), 4-chloronitrobenzene(4-ClNB), 4-cyanonitrobenzene (4-CNNB), 4-acetylnitrobenzene (4-AcNB), 4-bromonitrobenzene (4-BrNB), 4-nitrotoluene (4-MeNB). ''<sup>b</sup>'' Initial aqueous Fe(II). ''<sup>c</sup>'' Aqueous Fe(II) after 24h of equilibration. ''<sup>d</sup>'' Difference between b and c. ''<sup>e</sup>'' Initial nominal NAC concentration. ''<sup>f</sup>'' Pseudo-first order rate constant. ''<sup>g</sup>'' Surface area normalized rate constant calculated as ''k<sub>Obs</sub>'' '''/''' (surface area × mineral loading). | |
| | |} | | |} |
| | + | </br> |
| | + | The PRD reaction has been validated at the bench scale for the destruction of PFAS in a variety of environmental samples from Department of Defense sites (Table 1). Enspired Solutions<small><sup>TM</sup></small> has designed and manufactured a fully automatic commercial-scale piece of equipment called PFASigator<small><sup>TM</sup></small>, specializing in PRD PFAS destruction (Figure 2). This equipment is modular and scalable, has a small footprint, and can be used alone or in series with existing water treatment trains. The PFASigator<small><sup>TM</sup></small> employs commercially available UV reactors and monitoring meters that have been used in the water industry for decades. The system has been tested on PRD efficiency operational parameters, and key metrics were proven to be consistent with benchtop studies. |
| | | | |
| − | Iron(II) can be complexed by a myriad of organic ligands and may thereby become more reactive towards MCs and other pollutants. The reactivity of an Fe(II)-organic complex depends on the relative preference of the organic ligand for Fe(III) versus Fe(II)<ref name="Kim2009"/>. Since the majority of naturally occurring ligands complex Fe(III) more strongly than Fe(II), the reduction potential of the resulting Fe(III) complex is lower than that of aqueous Fe(III); therefore, complexation by organic ligands often renders Fe(II) a stronger reductant thermodynamically<ref name="Strathmann2011">Strathmann, T.J., 2011. Redox Reactivity of Organically Complexed Iron(II) Species with Aquatic Contaminants. Aquatic Redox Chemistry, American Chemical Society,1071(14), pp. 283-313. [https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-2011-1071.ch014 DOI: 10.1021/bk-2011-1071.ch014]</ref>. The reactivity of dissolved Fe(II)-organic complexes towards NACs/MCs has been investigated. The intrinsic, second-order rate constants and one electron reduction potentials are listed in Table 2.
| + | Bench scale PRD tests were performed for the following samples collected from Department of Defense sites: groundwater (GW), groundwater foam fractionate (FF), firefighting truck rinsate ([[Wikipedia: Firefighting foam | AFFF]] Rinsate), 3M Lightwater AFFF, investigation derived waste nanofiltrate (IDW NF), [[Wikipedia: Ion exchange | ion exchange]] still bottom (IX SB), and Ansulite AFFF. The PRD treatment was more effective in low conductivity/TDS solutions. Generally, PRD reaction rates decrease for solutions with a TDS > 10,000 ppm, with an upper limit of 30,000 ppm. Ansulite AFFF and IX SB samples showed low destruction efficiencies during initial screening tests, which was primarily attributed to their high TDS concentrations. Benchtop testing data are shown in Table 1 for the remaining five sample matrices. |
| − | | |
| − | In addition to forming organic complexes, iron is ubiquitous in minerals. Iron-bearing minerals play an important role in controlling the environmental fate of contaminants through adsorption<ref name="Linker2015">Linker, B.R., Khatiwada, R., Perdrial, N., Abrell, L., Sierra-Alvarez, R., Field, J.A., and Chorover, J., 2015. Adsorption of novel insensitive munitions compounds at clay mineral and metal oxide surfaces. Environmental Chemistry, 12(1), pp. 74–84. [https://doi.org/10.1071/EN14065 DOI: 10.1071/EN14065]</ref><ref name="Jenness2020">Jenness, G.R., Giles, S.A., and Shukla, M.K., 2020. Thermodynamic Adsorption States of TNT and DNAN on Corundum and Hematite. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 124(25), pp. 13837–13844. [https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c04512 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c04512]</ref> and reduction<ref name="Gorski2011">Gorski, C.A., and Scherer, M.M., 2011. Fe<sup>2+</sup> Sorption at the Fe Oxide-Water Interface: A Revised Conceptual Framework. Aquatic Redox Chemistry, American Chemical Society, 1071(15), pp. 315–343. [https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-2011-1071.ch015 DOI: 10.1021/bk-2011-1071.ch015]</ref> processes. Studies have shown that aqueous Fe(II) itself cannot reduce NACs/MCs at circumneutral pH<ref name="Klausen1995"/><ref name="Gregory2004">Gregory, K.B., Larese-Casanova, P., Parkin, G.F., and Scherer, M.M., 2004. Abiotic Transformation of Hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine by Fe<sup>II</sup> Bound to Magnetite. Environmental Science and Technology, 38(5), pp. 1408–1414. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es034588w DOI: 10.1021/es034588w]</ref> but in the presence of an iron oxide (e.g., goethite, hematite, lepidocrocite, ferrihydrite, or magnetite), NACs<ref name="Colón2006"/><ref name="Klausen1995"/><ref name="Strehlau2016"/><ref name="Elsner2004"/><ref name="Hofstetter2006"/> and MCs such as TNT<ref name="Hofstetter1999"/>, RDX<ref name="Gregory2004"/>, DNAN<ref name="Berens2019">Berens, M.J., Ulrich, B.A., Strehlau, J.H., Hofstetter, T.B., and Arnold, W.A., 2019. Mineral identity, natural organic matter, and repeated contaminant exposures do not affect the carbon and nitrogen isotope fractionation of 2,4-dinitroanisole during abiotic reduction. Environmental Science: Processes and Impacts, 21(1), pp. 51-62. [https://doi.org/10.1039/C8EM00381E DOI: 10.1039/C8EM00381E]</ref>, and NG<ref name="Oh2004">Oh, S.-Y., Cha, D.K., Kim, B.J., and Chiu, P.C., 2004. Reduction of Nitroglycerin with Elemental Iron: Pathway, Kinetics, and Mechanisms. Environmental Science and Technology, 38(13), pp. 3723–3730. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es0354667 DOI: 10.1021/es0354667]</ref> can be rapidly reduced. Unlike ferric oxides, Fe(II)-bearing minerals including clays<ref name="Hofstetter2006"/><ref name="Schultz2000"/><ref name="Luan2015a"/><ref name="Luan2015b"/><ref name="Hofstetter2003"/><ref name="Neumann2008"/><ref name="Hofstetter2008"/>, green rust<ref name="Larese-Casanova2008"/><ref name="Khatiwada2018">Khatiwada, R., Root, R.A., Abrell, L., Sierra-Alvarez, R., Field, J.A., and Chorover, J., 2018. Abiotic reduction of insensitive munition compounds by sulfate green rust. Environmental Chemistry, 15(5), pp. 259–266. [https://doi.org/10.1071/EN17221 DOI: 10.1071/EN17221]</ref>, mackinawite<ref name="Elsner2004"/><ref name="Berens2019"/><ref name="Menezes2021">Menezes, O., Yu, Y., Root, R.A., Gavazza, S., Chorover, J., Sierra-Alvarez, R., and Field, J.A., 2021. Iron(II) monosulfide (FeS) minerals reductively transform the insensitive munitions compounds 2,4-dinitroanisole (DNAN) and 3-nitro-1,2,4-triazol-5-one (NTO). Chemosphere, 285, p. 131409. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131409 DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131409]</ref> and pyrite<ref name="Elsner2004"/><ref name="Oh2008">Oh, S.-Y., Chiu, P.C., and Cha, D.K., 2008. Reductive transformation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene, hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine, and nitroglycerin by pyrite and magnetite. Journal of hazardous materials, 158(2-3), pp. 652–655. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.01.078 DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.01.078]</ref> do not need aqueous Fe(II) to be reactive toward NACs/MCs. However, upon oxidation, sulfate green rust was converted into lepidocrocite<ref name="Khatiwada2018"/>, and mackinawite into goethite<ref name="Menezes2021"/>, suggesting that aqueous Fe(II) coupled to Fe(III) oxides might be at least partially responsible for continued degradation of NACs/MCs in the subsurface once the parent reductant (e.g., green rust or iron sulfide) oxidizes.
| |
| | | | |
| − | The reaction conditions and rate constants for a list of studies on MC reduction by iron oxide-aqueous Fe(II) redox couples and by other Fe(II)-containing minerals are shown in Table 3<ref name="Hofstetter1999"/><ref name="Larese-Casanova2008"/><ref name="Gregory2004"/><ref name="Berens2019"/><ref name="Oh2008"/><ref name="Strehlau2018">Strehlau, J.H., Berens, M.J., and Arnold, W.A., 2018. Mineralogy and buffer identity effects on RDX kinetics and intermediates during reaction with natural and synthetic magnetite. Chemosphere, 213, pp. 602–609. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.09.139 DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.09.139]</ref><ref name="Cardenas-Hernandez2020">Cárdenas-Hernandez, P.A., Anderson, K.A., Murillo-Gelvez, J., di Toro, D.M., Allen, H.E., Carbonaro, R.F., and Chiu, P.C., 2020. Reduction of 3-Nitro-1,2,4-Triazol-5-One (NTO) by the Hematite–Aqueous Fe(II) Redox Couple. Environmental Science and Technology, 54(19), pp. 12191–12201. [https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c03872 DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.0c03872]</ref>. Unlike hydroquinones and Fe(II) complexes, where second-order rate constants can be readily calculated, the reduction rate constants of NACs/MCs in mineral suspensions are often specific to the experimental conditions used and are usually reported as BET surface area-normalized reduction rate constants (''k<sub>SA</sub>''). In the case of iron oxide-Fe(II) redox couples, reduction rate constants have been shown to increase with pH (specifically, with [OH<sup>– </sup>]<sup>2</sup>) and aqueous Fe(II) concentration, both of which correspond to a decrease in the system's reduction potential<ref name="Colón2006"/><ref name="Gorski2016"/><ref name="Cardenas-Hernandez2020"/>.
| + | During treatment, PFOS and PFOA concentrations decreased 96% to >99% and 77% to 97%, respectively. For the PFAS with proposed drinking water Maximum Contaminant Levels (MCLs) recently established by the USEPA (PFNA, PFOA, PFOS, PFHxS, PFBS, and HFPO-DA), concentrations decreased >99% for GW, 93% for FF, 95% for AFFF Rinsate and IDW NF, and 79% for AFFF (diluted 10x) during the treatment time allotted. Meanwhile, the total PFAS concentrations, including all 40 known PFAS analytes and unidentified perfluorocarboxylic acid (PFCA) precursors, decreased from 34% to 96% following treatment. All of these concentration reduction values were calculated by using reporting limits (RL) as the concentrations for non-detects. |
| | | | |
| − | For minerals that contain structural iron(II) and can reduce pollutants in the absence of aqueous Fe(II), the observed rates of reduction increased with increasing structural Fe(II) content, as seen with iron-bearing clays<ref name="Luan2015a"/><ref name="Luan2015b"/> and green rust<ref name="Larese-Casanova2008"/>. This dependency on Fe(II) content allows for the derivation of second-order rate constants, as shown on Table 3 for the reduction of RDX by green rust<ref name="Larese-Casanova2008"/>, and the development of reduction potential (E<sub>H</sub>)-based models<ref name="Luan2015a"/><ref name="Gorski2012a">Gorski, C.A., Aeschbacher, M., Soltermann, D., Voegelin, A., Baeyens, B., Marques Fernandes, M., Hofstetter, T.B., and Sander, M., 2012. Redox Properties of Structural Fe in Clay Minerals. 1. Electrochemical Quantification of Electron-Donating and -Accepting Capacities of Smectites. Environmental Science and Technology, 46(17), pp. 9360–9368. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es3020138 DOI: 10.1021/es3020138]</ref><ref name="Gorski2012b">Gorski, C.A., Klüpfel, L., Voegelin, A., Sander, M., and Hofstetter, T.B., 2012. Redox Properties of Structural Fe in Clay Minerals. 2. Electrochemical and Spectroscopic Characterization of Electron Transfer Irreversibility in Ferruginous Smectite, SWa-1. Environmental Science and Technology, 46(17), pp. 9369–9377. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es302014u DOI: 10.1021/es302014u]</ref><ref name="Gorski2013">Gorski, C.A., Klüpfel, L.E., Voegelin, A., Sander, M. and Hofstetter, T.B., 2013. Redox Properties of Structural Fe in Clay Minerals: 3. Relationships between Smectite Redox and Structural Properties. Environmental Science and Technology, 47(23), pp. 13477–13485. [https://doi.org/10.1021/es403824x DOI: 10.1021/es403824x]</ref>, where E<sub>H</sub> represents the reduction potential of the iron-bearing clays. Iron-bearing expandable clay minerals represent a special case, which in addition to reduction can remove NACs/MCs through adsorption. This is particularly important for planar NACs/MCs that contain multiple electron-withdrawing nitro groups and can form strong electron donor-acceptor (EDA) complexes with the clay surface<ref name="Hofstetter2006"/><ref name="Hofstetter2003"/><ref name="Neumann2008"/>.
| + | Excellent fluorine/fluoride mass balance was achieved. There was nearly a 1:1 conversion of organic fluorine to free inorganic fluoride ion during treatment of GW, FF and AFFF Rinsate. The 3M Lightwater AFFF (diluted 10x) achieved only 65% fluorine mass balance, but this was likely due to high adsorption of PFAS to the reactor. |
| | | | |
| − | Although the second-order rate constants derived for Fe(II)-bearing minerals may allow comparison among different studies, they may not reflect changes in reactivity due to variations in surface area, pH, and the presence of ions. Anions such as bicarbonate<ref name="Larese-Casanova2008"/><ref name="Strehlau2018"/><ref name="Chen2020">Chen, G., Hofstetter, T.B., and Gorski, C.A., 2020. Role of Carbonate in Thermodynamic Relationships Describing Pollutant Reduction Kinetics by Iron Oxide-Bound Fe<sup>2+</sup>. Environmental Science and Technology, 54(16), pp. 10109–10117. [https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c02959 DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.0c02959]</ref> and phosphate<ref name="Larese-Casanova2008"/><ref name="Bocher2004">Bocher, F., Géhin, A., Ruby, C., Ghanbaja, J., Abdelmoula, M., and Génin, J.M.R., 2004. Coprecipitation of Fe(II–III) hydroxycarbonate green rust stabilised by phosphate adsorption. Solid State Sciences, 6(1), pp. 117–124. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2003.10.004 DOI: 10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2003.10.004]</ref> are known to decrease the reactivity of iron oxides-Fe(II) redox couples and green rust. Sulfite has also been shown to decrease the reactivity of hematite-Fe(II) towards the deprotonated form of NTO (Table 3)<ref name="Cardenas-Hernandez2020"/>. Exchanging cations in iron-bearing clays can change the reactivity of these minerals by up to 7-fold<ref name="Hofstetter2006"/>. Thus, more comprehensive models are needed to account for the complexities in the subsurface environment.
| + | ===Application=== |
| | + | Due to the first-order kinetics of PRD, destruction of PFAS is most energy efficient when paired with a pre-concentration technology, such as foam fractionation (FF), nanofiltration, reverse osmosis, or resin/carbon adsorption, that remove PFAS from water. Application of the PFASigator<small><sup>TM</sup></small> is therefore proposed as a part of a PFAS treatment train that includes a pre-concentration step. |
| | | | |
| − | The reduction of NACs has been widely studied in the presence of different iron minerals, pH, and Fe(II)<sub>(aq)</sub> concentrations (Table 4)<ref name="Colón2006"/><ref name="Klausen1995"/><ref name="Strehlau2016"/><ref name="Elsner2004"/><ref name="Hofstetter2006"/>. Only selected NACs are included in Table 4. For more information on other NACs and ferruginous reductants, please refer to the cited references. | + | The first pilot study with the PFASigator<small><sup>TM</sup></small> was conducted in late 2023 at an industrial facility in Michigan with PFAS-impacted groundwater. The goal of the pilot study was to treat the groundwater to below the limits for regulatory discharge permits. For the pilot demonstration, the PFASigator<small><sup>TM</sup></small> was paired with an FF unit, which pre-concentrated the PFAS into a foamate that was pumped into the PFASigator<small><sup>TM</sup></small> for batch PFAS destruction. Residual PFAS remaining after the destruction batch was treated by looping back the PFASigator<small><sup>TM</sup></small> effluent to the FF system influent. During the one-month field pilot duration, site-specific discharge limits were met, and steady state operation between the FF unit and PFASigator<small><sup>TM</sup></small> was achieved such that the PFASigator<small><sup>TM</sup></small> destroyed the required concentrated PFAS mass and no off-site disposal of PFAS contaminated waste was required. |
| | | | |
| | ==References== | | ==References== |